How Does Biodiversity Affect The Stability Of An Ecosystem
Introduction
How Does Biodiversity Affect The Stability Of An Ecosystem: Biodiversity refers to the variety of living organisms in a particular ecosystem. It encompasses the different species of plants, animals, and microorganisms that coexist and interact within a given habitat. The stability of an ecosystem, on the other hand, refers to its ability to maintain its structure and function over time, despite disturbances or changes in environmental conditions. Understanding the relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem stability is crucial for conservation efforts and sustainable management of natural resources.
One of the key ways in which biodiversity affects ecosystem stability is through its role in providing essential ecosystem services. Ecosystem services are the benefits that humans derive from nature, such as clean air and water, pollination of crops, and regulation of climate. Biodiversity plays a critical role in maintaining these services by ensuring the resilience and adaptability of ecosystems. For example, a diverse community of plants can better withstand changes in temperature, rainfall patterns, and nutrient availability, thereby reducing the risk of ecosystem collapse.
Furthermore, biodiversity contributes to ecosystem stability by enhancing the efficiency and productivity of ecological processes. Each species in an ecosystem has a unique set of traits and functions that contribute to the overall functioning of the system. For instance, certain plant species may have deep root systems that help prevent soil erosion, while others may have specialized adaptations for nutrient cycling. The presence of a diverse array of species ensures that these functions are carried out effectively, making the ecosystem more resistant to disturbances and better able to recover from them.
However, the relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem stability is not always straightforward. In some cases, high levels of biodiversity can actually make an ecosystem more vulnerable to disturbances. This is because complex ecosystems with many interacting species may be more prone to cascading effects, where the loss of one species can have far-reaching consequences for the entire system. Understanding these complexities and the trade-offs involved is essential for effective conservation and management strategies.

How does biodiversity affect the stability of an ecosystem quizlet?
How does biodiversity affect the stability of an ecosystem? Having a number of different organisms increases the stability of an ecosystem, because a change in the population of one organism will have less effect on the population of an organism that depends on it.
Biodiversity refers to the variety of living organisms in a particular area, including plants, animals, and microorganisms. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the stability of an ecosystem. The stability of an ecosystem refers to its ability to resist and recover from disturbances, such as natural disasters or human activities. Biodiversity affects the stability of an ecosystem in several ways.
Firstly, a high level of biodiversity increases the resilience of an ecosystem. Resilience refers to the ability of an ecosystem to bounce back and recover after a disturbance. In a diverse ecosystem, different species have different roles and functions. If one species is negatively affected by a disturbance, other species can compensate for its loss and maintain the overall functioning of the ecosystem. This ensures that the ecosystem remains stable and can continue to provide essential services, such as clean air and water, food production, and climate regulation.
Secondly, biodiversity enhances the stability of an ecosystem by increasing its resistance to invasive species. Invasive species are non-native species that can outcompete and displace native species, leading to a loss of biodiversity. A diverse ecosystem is more resistant to invasive species because there are more species competing for resources, making it harder for any one species to dominate. This resistance to invasive species helps maintain the balance and stability of the ecosystem.
Thirdly, biodiversity contributes to the stability of an ecosystem by increasing its productivity. In a diverse ecosystem, different species have different ecological roles, such as pollination, nutrient cycling, and pest control. Each species contributes to the overall functioning of the ecosystem, and their interactions create a web of relationships that support productivity. If one species declines or disappears, it can disrupt these interactions and reduce the productivity of the ecosystem. Therefore, a high level of biodiversity is essential for maintaining the stability and productivity of an ecosystem.
How does biodiversity affect the stability of an ecosystem essay?
Greater biodiversity in ecosystems, species, and individuals leads to greater stability. For example, species with high genetic diversity and many populations that are adapted to a wide variety of conditions are more likely to be able to weather disturbances, disease, and climate change.
Biodiversity refers to the variety of living organisms in a particular ecosystem. It encompasses the different species of plants, animals, and microorganisms that coexist and interact within a given habitat. The stability of an ecosystem is greatly influenced by its biodiversity, as each species plays a unique role in maintaining the overall balance and functioning of the system.
Biodiversity is essential for the stability of an ecosystem due to several reasons. Firstly, a diverse range of species ensures that there are multiple pathways for energy flow and nutrient cycling within the ecosystem. Each species has its own specific role in the food web, and the interactions between different species help to maintain the overall structure and functioning of the ecosystem. For example, predators help to control the population of prey species, preventing them from becoming too abundant and causing imbalances in the ecosystem.
Furthermore, biodiversity also enhances the resilience of an ecosystem to environmental changes and disturbances. A diverse ecosystem is better able to withstand and recover from disturbances such as natural disasters or human activities. This is because different species have different adaptations and tolerances to various environmental conditions. If one species is negatively affected by a disturbance, other species may be able to compensate for its loss and maintain the stability of the ecosystem.
Additionally, biodiversity provides a range of ecosystem services that are essential for human well-being. These services include the provision of food, clean water, and air, as well as the regulation of climate and disease. A diverse ecosystem is more likely to be able to provide these services sustainably, as different species contribute to different aspects of ecosystem functioning. For example, plants play a crucial role in carbon sequestration and oxygen production, while insects are important pollinators of crops.
Biodiversity is crucial for the stability of an ecosystem. It ensures the efficient functioning of energy and nutrient cycles, enhances the resilience of the ecosystem to disturbances, and provides essential ecosystem services. Therefore, it is important to conserve and protect biodiversity to maintain the stability and sustainability of ecosystems.
Does biodiversity increase stability?
Greater biodiversity in ecosystems, species, and individuals leads to greater stability. For example, species with high genetic diversity and many populations that are adapted to a wide variety of conditions are more likely to be able to weather disturbances, disease, and climate change.
Introduction:
Biodiversity refers to the variety of living organisms in a particular ecosystem. It encompasses the diversity of species, genes, and ecosystems. Stability, on the other hand, refers to the ability of an ecosystem to resist and recover from disturbances. The relationship between biodiversity and stability has been a topic of much debate and research in the field of ecology.
One school of thought argues that biodiversity increases stability in ecosystems. This is based on the idea that a greater number of species within an ecosystem provides a wider range of functional traits and ecological roles. This diversity of species ensures that there are multiple pathways for energy flow and nutrient cycling, making the ecosystem more resilient to disturbances. Additionally, different species may have different responses to environmental changes, so a diverse ecosystem is more likely to have some species that can thrive under changing conditions.
Another perspective suggests that biodiversity does not necessarily increase stability. This viewpoint argues that stability is more dependent on the interactions and dynamics between species rather than the number of species present. According to this perspective, stability is determined by the strength and complexity of ecological interactions, such as predation, competition, and mutualism. Therefore, even a relatively low-diversity ecosystem can be stable if the interactions between species are well-balanced and resilient.
However, it is important to note that the relationship between biodiversity and stability is complex and can vary depending on the specific context and scale of analysis. Some studies have found a positive correlation between biodiversity and stability, while others have found no significant relationship or even a negative relationship. Factors such as the type of disturbance, the level of biodiversity, and the spatial and temporal scales of analysis can all influence the relationship.
What can affect the stability of an ecosystem?
Factors affecting stability:
Disturbance frequency and intensity (how often and what kind of tillage) Species diversity (intercropping or rotations), interactions (competition for water and nutrients from weed species), and life history strategies (do the species grow fast and produce many seeds or slow with few seeds)
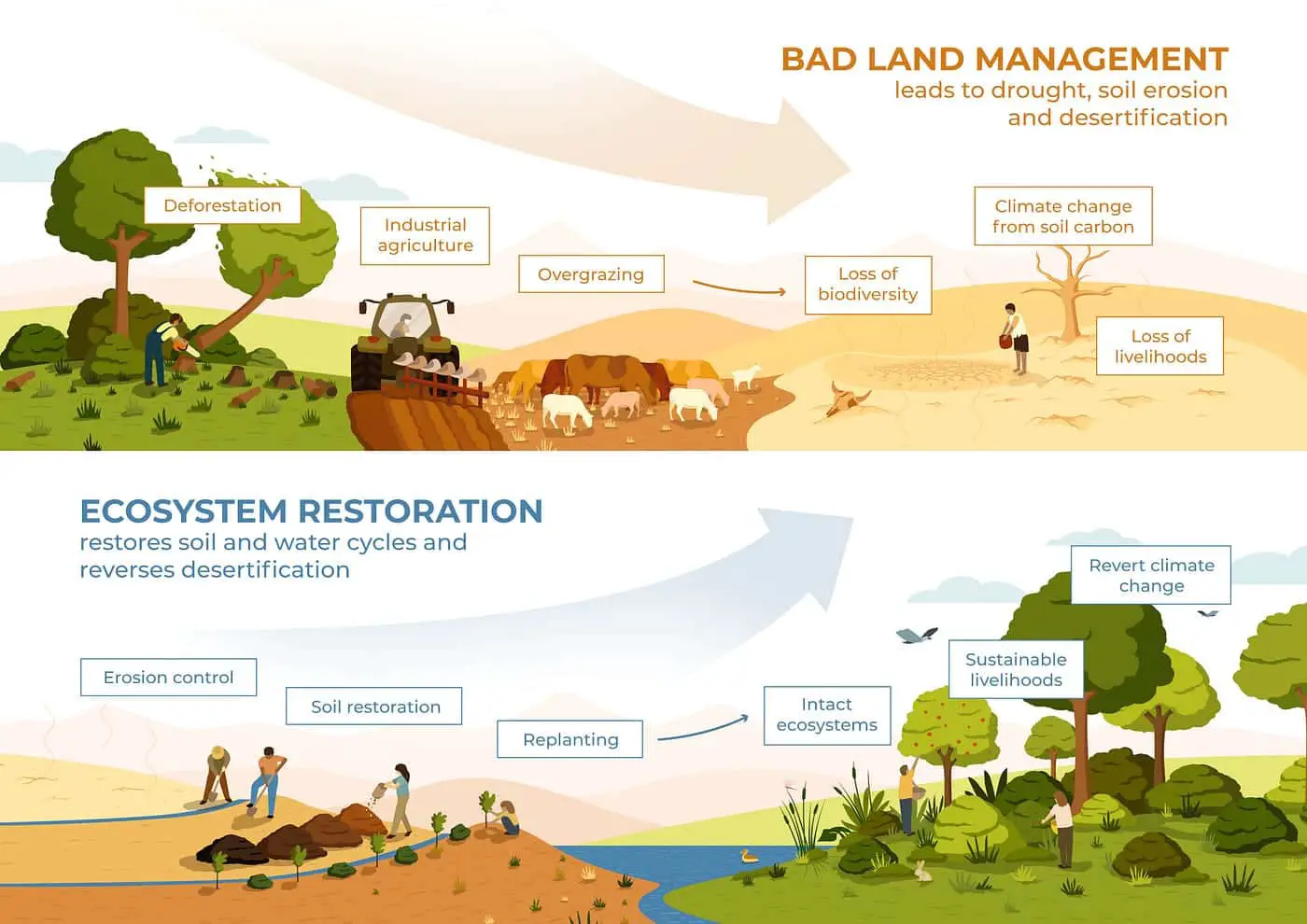
An ecosystem is a complex network of living organisms, their physical environment, and the interactions between them. It is a delicate balance that can be easily disrupted by various factors. Several factors can affect the stability of an ecosystem, including natural disasters, human activities, invasive species, pollution, and climate change.
Natural disasters such as hurricanes, earthquakes, floods, and wildfires can have a significant impact on the stability of an ecosystem. These events can destroy habitats, kill or displace organisms, and disrupt the natural processes that maintain balance within the ecosystem. For example, a wildfire can destroy a forest, leading to the loss of plant and animal species that depend on that habitat.
Human activities can also have a profound effect on the stability of an ecosystem. Deforestation, urbanization, agriculture, and industrialization can all lead to habitat destruction and fragmentation. When natural habitats are destroyed or altered, many species may lose their homes and sources of food, leading to population declines or even extinction. Additionally, activities such as overfishing, hunting, and pollution can disrupt the delicate balance of an ecosystem.
Invasive species are another factor that can affect the stability of an ecosystem. These are non-native species that are introduced into an ecosystem and can outcompete native species for resources. Invasive species can disrupt the natural balance of an ecosystem by preying on native species, competing for food and habitat, and spreading diseases. This can lead to a decline in native species populations and a loss of biodiversity.
Pollution is a major threat to the stability of ecosystems. Pollution can come in many forms, including air pollution, water pollution, and soil pollution. Chemical pollutants can contaminate water sources, killing aquatic organisms and disrupting the food chain. Air pollution can harm plants and animals, leading to reduced biodiversity. Soil pollution can affect the health of plants and the organisms that depend on them.
Climate change is perhaps one of the most significant factors affecting the stability of ecosystems. Rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events can all have profound effects on ecosystems. These changes can alter the distribution and abundance of species, disrupt natural processes such as pollination and seed dispersal, and lead to the loss of habitats. Climate change can also exacerbate other factors that affect ecosystem stability, such as”
What is ecosystem stability in biodiversity?
Ecosystem stability is the ability of an ecosystem to maintain a steady state, even after a stress or disturbance has occurred.17
Ecosystem stability in biodiversity refers to the ability of an ecosystem to maintain its structure and function over time, despite disturbances or changes in environmental conditions. It is a measure of the resilience and resistance of an ecosystem to external pressures, such as climate change, habitat loss, or species extinction. Ecosystem stability is crucial for the survival and well-being of all organisms within the ecosystem, as it ensures the availability of essential resources and services.
Biodiversity is the variety of life forms and processes that exist within an ecosystem. It includes the diversity of species, genes, and ecosystems, and the interactions between them. Biodiversity is essential for the functioning of ecosystems and the provision of ecosystem services, such as clean air and water, nutrient cycling, and climate regulation. Ecosystem stability is closely linked to biodiversity, as a diverse and balanced ecosystem is more likely to be stable and resilient to disturbances.
One of the key factors that contribute to ecosystem stability in biodiversity is species diversity. A high number of species within an ecosystem provides a greater variety of ecological niches and functional roles, which increases the overall stability of the ecosystem. Each species has its own unique set of adaptations and interactions with other species, which helps to maintain the balance and functioning of the ecosystem. In contrast, a loss of species diversity can lead to imbalances and disruptions in the ecosystem, making it more vulnerable to disturbances.
Habitat diversity is another important aspect of ecosystem stability in biodiversity. Different habitats within an ecosystem provide a range of resources and conditions for different species, allowing them to coexist and thrive. A diverse habitat structure also promotes the movement and dispersal of species, which helps to maintain genetic diversity and reduce the risk of inbreeding. Loss or degradation of habitats can disrupt these processes and reduce the stability of the ecosystem.
Climate stability is also crucial for ecosystem stability in biodiversity. Changes in climate patterns, such as temperature, precipitation, and extreme weather events, can have profound impacts on ecosystems and the species within them. Ecosystems that are adapted to specific climate conditions may struggle to cope with rapid or extreme changes, leading to shifts in species composition and ecosystem functioning. Therefore, maintaining stable climate conditions is essential for the long-term stability and survival of ecosystems.
What is the relationship between biodiversity and the stability of an ecosystem?
Biodiversity refers to the variety of species and genetic diversity within an ecosystem. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the stability of an ecosystem. A diverse range of species provides a greater number of interactions and relationships within the ecosystem, creating a complex web of interdependencies. This complexity enhances the stability of the ecosystem by increasing its resilience and resistance to disturbances.
Firstly, a high level of biodiversity ensures that there are multiple species performing similar ecological functions. This redundancy acts as a buffer against the loss of any one species. If a particular species is negatively affected by a disturbance, other species with similar functions can compensate for the loss, maintaining the overall stability of the ecosystem. Additionally, a diverse range of species increases the efficiency of resource utilization within the ecosystem, reducing competition and enhancing stability.
How does the presence of a diverse range of species impact the stability of an ecosystem?
The presence of a diverse range of species has a significant impact on the stability of an ecosystem. Biodiversity plays a crucial role in maintaining the overall health and functioning of an ecosystem. When there is a high level of species diversity, it ensures that there are multiple ecological niches filled, which leads to a more stable and resilient ecosystem. Each species has its own unique role and function within the ecosystem, and the interactions between different species help to maintain a balance.
Firstly, a diverse range of species provides a greater variety of resources and services to the ecosystem. For example, different plant species contribute to the production of oxygen, the absorption of carbon dioxide, and the prevention of soil erosion. In turn, these services support the survival and well-being of other organisms within the ecosystem. Additionally, a diverse range of species also enhances the stability of food webs and nutrient cycling. If one species declines or disappears, there are other species that can step in and fulfill similar roles, preventing the collapse of the entire ecosystem.
In what ways does biodiversity contribute to the overall resilience and resistance of an ecosystem?
Biodiversity plays a crucial role in enhancing the overall resilience and resistance of an ecosystem. Firstly, a diverse range of species ensures that there are multiple ecological functions and processes occurring within the ecosystem. This means that if one species or function is disrupted or lost, there are others that can compensate and maintain the overall stability of the ecosystem. For example, in a forest ecosystem, a diverse range of tree species ensures that if one species is affected by a disease or pest, other species can continue to provide important ecosystem services such as carbon sequestration and habitat for other organisms.
Furthermore, biodiversity contributes to the resilience and resistance of an ecosystem by increasing its ability to withstand and recover from disturbances. Ecosystems with higher biodiversity tend to have a greater variety of genetic traits and adaptations, which allows them to better cope with changes in environmental conditions. This means that they are more likely to recover quickly after a disturbance, such as a natural disaster or human-induced disturbance. Additionally, a diverse range of species can also provide a buffer against invasive species or diseases, as they can outcompete or resist the establishment of these threats.
Can a decrease in biodiversity lead to a decline in the stability of an ecosystem? If so, how?
Yes, a decrease in biodiversity can indeed lead to a decline in the stability of an ecosystem. Biodiversity refers to the variety of species and genetic diversity within an ecosystem. When there is a decrease in biodiversity, it means that certain species are becoming extinct or their populations are declining. This can have significant negative impacts on the stability of the ecosystem.
Firstly, a decrease in biodiversity can disrupt the delicate balance of an ecosystem. Each species plays a unique role in the ecosystem, and their interactions with other species are often complex and interdependent. When a species becomes extinct or its population declines, it can disrupt the food chain and other ecological processes. This can lead to a cascade of negative effects throughout the ecosystem, ultimately destabilizing it.
Furthermore, a decrease in biodiversity can also reduce the resilience and resistance of an ecosystem. Biodiversity provides a buffer against environmental changes and disturbances. A diverse range of species means that there are more options for adaptation and recovery when faced with challenges such as climate change or disease outbreaks. However, when biodiversity decreases, the ecosystem becomes more vulnerable to these disturbances, making it less stable in the long run.
Are there any specific examples or case studies that demonstrate the direct link between biodiversity and the stability of an ecosystem?
Yes, there are several examples and case studies that demonstrate the direct link between biodiversity and the stability of an ecosystem. One such example is the study conducted by ecologists at the University of California, Santa Barbara, which examined the impact of biodiversity on the stability of marine ecosystems. The researchers found that areas with higher levels of biodiversity were more resistant to disturbances such as disease outbreaks and extreme weather events. This is because a diverse range of species provides a greater variety of ecological functions and interactions, which can help buffer the ecosystem against disruptions.
Another example is the case study of the Yellowstone National Park in the United States. When wolves were reintroduced into the park in the 1990s, it had a profound effect on the ecosystem. The presence of wolves led to a decrease in the population of herbivores such as elk, which in turn allowed for the recovery of vegetation and the return of other species such as beavers and songbirds. This cascade of effects demonstrated how the presence of a top predator can regulate the population dynamics of other species and promote overall ecosystem stability.

Conclusion
Biodiversity refers to the variety of living organisms in a particular ecosystem. It encompasses the different species, genes, and ecosystems that exist within a given area. The stability of an ecosystem, on the other hand, refers to its ability to maintain its structure and function over time, despite disturbances or changes in environmental conditions. The relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem stability is a complex and dynamic one, with numerous factors influencing their interplay.
One of the key ways in which biodiversity affects the stability of an ecosystem is through its role in providing various ecosystem services. Ecosystem services are the benefits that humans derive from ecosystems, such as clean air and water, pollination of crops, and regulation of climate. Biodiversity plays a crucial role in the provision of these services, as different species have different functional roles within an ecosystem. For example, a diverse community of plants can help stabilize soil, prevent erosion, and regulate water flow, thus reducing the impacts of floods and droughts. Similarly, a diverse community of pollinators, such as bees and butterflies, is essential for the pollination of crops and the production of food.
Furthermore, biodiversity can enhance the resilience of an ecosystem to disturbances. A diverse ecosystem is better able to withstand and recover from disturbances, such as natural disasters or human-induced changes. This is because different species have different responses to disturbances, and a diverse community is more likely to have some species that are able to adapt and survive in changing conditions. In contrast, a less diverse ecosystem may be more vulnerable to disturbances, as it may lack the necessary resilience and adaptive capacity to recover.
However, the relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem stability is not always straightforward. In some cases, high levels of biodiversity can actually decrease ecosystem stability. This can occur when certain species become dominant and outcompete others, leading to a loss of diversity and a decrease in the overall stability of the ecosystem. Additionally, the loss of keystone species, which play a critical role in maintaining the structure and function of an ecosystem, can have cascading effects on the stability of the entire ecosystem.
Discover the intricate relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem stability. Explore how the presence and abundance of diverse species impact the overall resilience and balance of an ecosystem.



