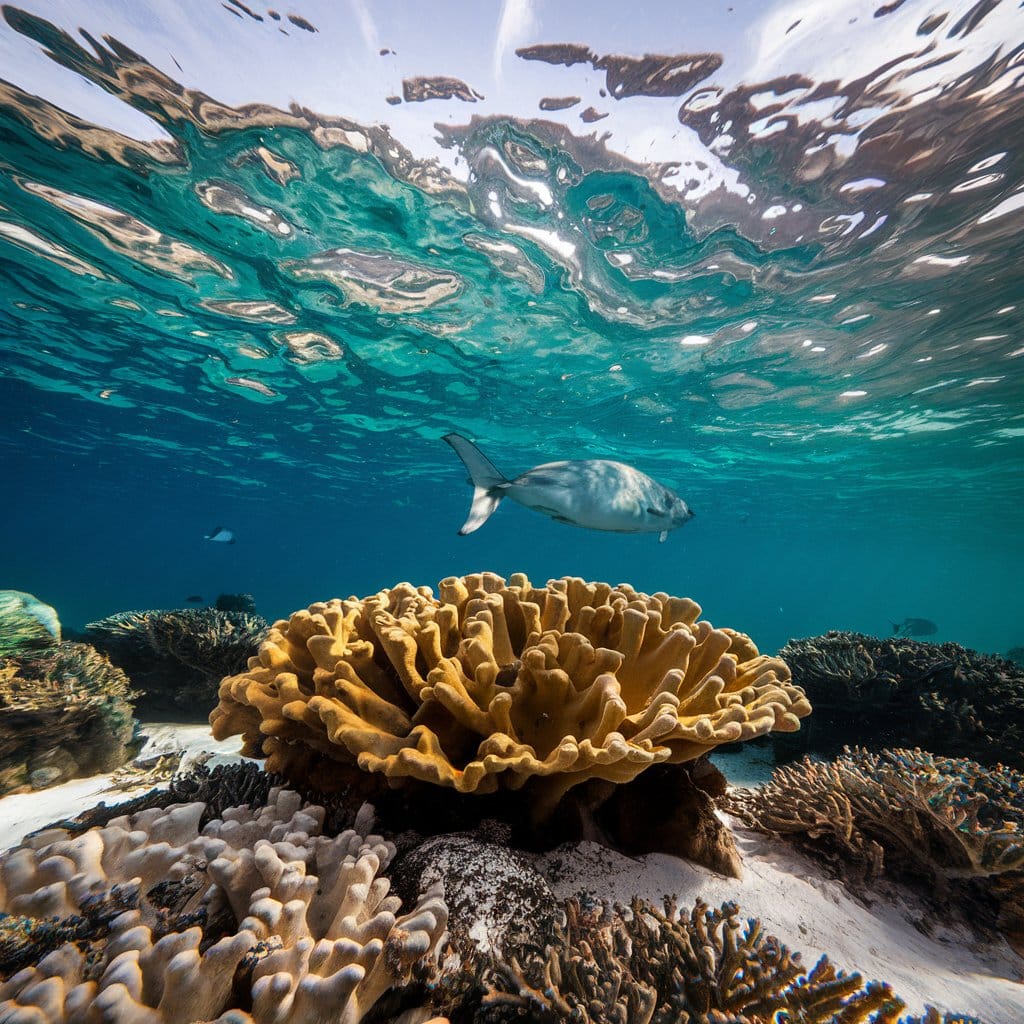
What Does High Biodiversity Mean
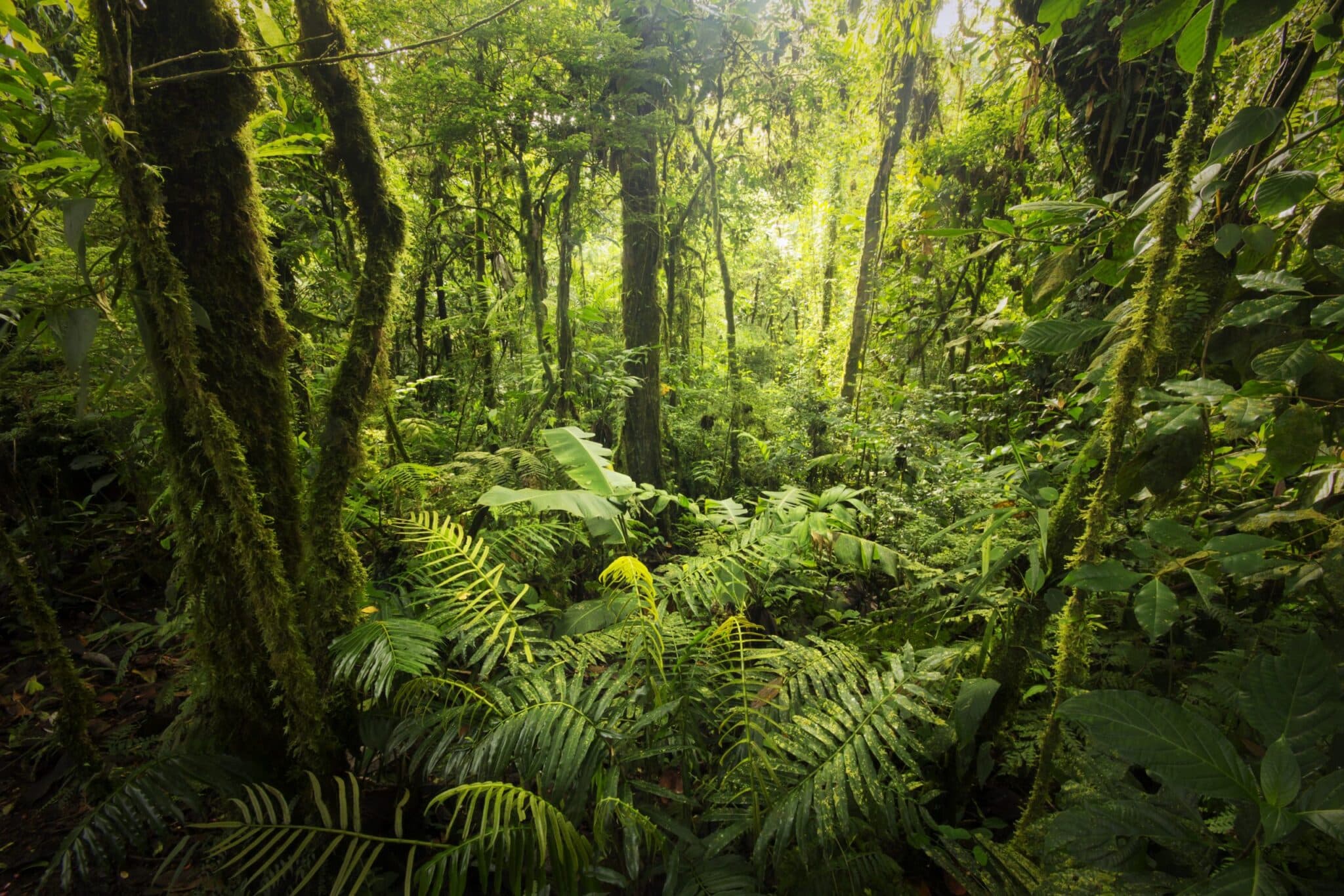

Introduction
What Does High Biodiversity Mean: Biodiversity refers to the variety of life forms present on Earth, including plants, animals, and microorganisms. It encompasses the genetic, species, and ecosystem diversity that exists in different habitats and ecosystems. High biodiversity, therefore, refers to an area or region that has a rich and diverse range of species and ecosystems.
High biodiversity is often considered a measure of the health and resilience of an ecosystem. It indicates the presence of a wide range of species that are adapted to different environmental conditions and can perform various ecological functions. These functions include pollination, seed dispersal, nutrient cycling, and pest control, among others. The more diverse an ecosystem is, the better it can withstand disturbances and adapt to changing environmental conditions.
High biodiversity also provides numerous benefits to human societies. It is a source of food, medicine, and other valuable resources. Many of the medicines we use today are derived from plants and animals found in biodiverse regions. Additionally, biodiversity contributes to the cultural and aesthetic value of an area, attracting tourists and providing recreational opportunities.
However, high biodiversity is under threat due to various human activities, such as habitat destruction, pollution, climate change, and overexploitation of natural resources. These activities have led to the loss of species and ecosystems at an alarming rate, resulting in a decline in global biodiversity. The loss of biodiversity not only affects the functioning of ecosystems but also poses risks to human well-being, including food security, water availability, and climate regulation.
Efforts are being made worldwide to conserve and protect high biodiversity areas. Conservation strategies include the establishment of protected areas, sustainable management of natural resources, and the promotion of sustainable practices in agriculture, forestry, and fisheries. It is crucial to raise awareness about the importance of biodiversity and the need for its conservation to ensure the long-term survival of diverse species and ecosystems.
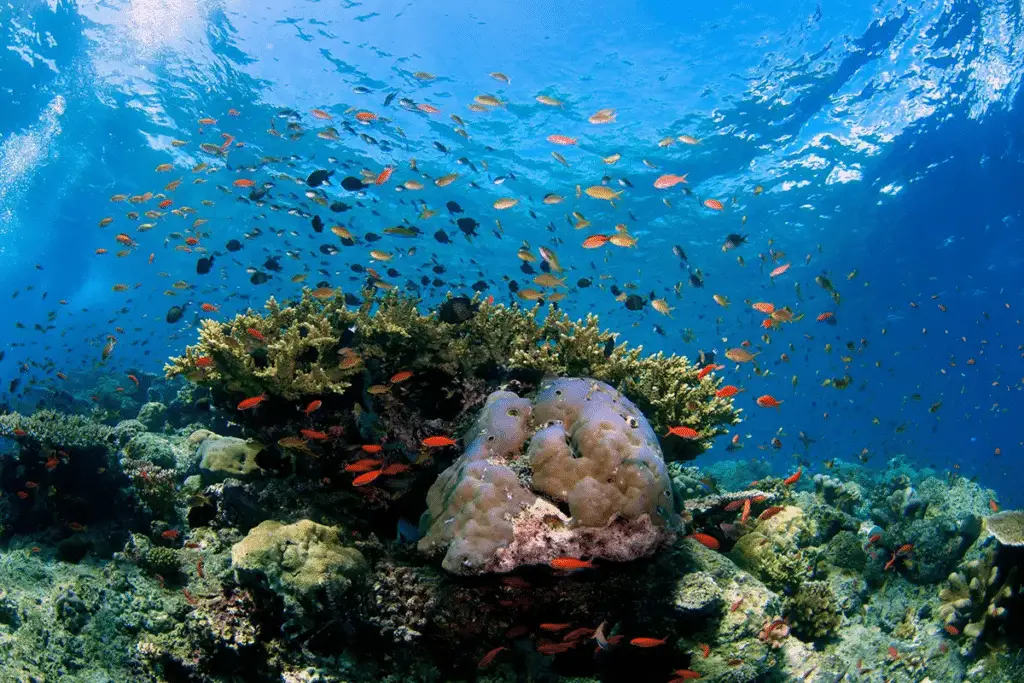

What is an example of high biodiversity?
Example of ecosystem with high biodiversity is tropical rain forest as seen in Amazon basin of south America. Such forests are also thriving in parts of central Africa and also in islands of Indonesia. In marine environment, coral reefs are example of high biodiversity aquatic ecosystems.
Biodiversity refers to the variety of life forms present in a particular ecosystem or on the entire planet. It encompasses the diversity of species, genes, and ecosystems. High biodiversity is a term used to describe an ecosystem or area that has a large number of different species and a wide range of genetic variation within those species. It is an indicator of a healthy and thriving ecosystem.
One example of an area with high biodiversity is the Amazon rainforest in South America. It is often referred to as the “lungs of the Earth” due to its vast size and the amount of oxygen it produces. The Amazon rainforest is home to an estimated 400 billion individual trees belonging to over 16,000 species. It is also home to countless species of animals, including jaguars, sloths, and macaws. The incredible diversity of plant and animal life in the Amazon rainforest is a testament to its high biodiversity.
Another example of high biodiversity can be found in the coral reefs of the Great Barrier Reef in Australia. The Great Barrier Reef is the largest coral reef system in the world and is home to an estimated 1,500 species of fish, 400 species of coral, and thousands of other marine species. The reef provides a habitat for a wide range of organisms, from tiny plankton to large sharks and whales. The intricate and delicate balance of life within the coral reef ecosystem is a prime example of high biodiversity.
The Galapagos Islands, located off the coast of Ecuador, are also known for their high biodiversity. The islands are famous for their unique and diverse array of plant and animal species, many of which are found nowhere else on Earth. The Galapagos Islands are home to giant tortoises, marine iguanas, and a variety of bird species, including the iconic blue-footed booby. The isolation of the islands has allowed for the evolution of distinct species, making it a hotspot for biodiversity.
In conclusion, high biodiversity can be found in various ecosystems around the world, such as the Amazon rainforest, the Great Barrier Reef, and the Galapagos Islands. These areas are characterized by a large number of different species and a wide range of genetic variation, making them important for the overall health and stability of the planet’s ecosystems.
What determines high biodiversity?
A common way to measure biodiversity is to count the total number of species living within a particular area. Tropical regions, areas that are warm year-round, have the most biodiversity. Temperate regions, which have warm summers and cold winters, have less biodiversity.
Biodiversity refers to the variety of life forms present in a particular ecosystem or on Earth as a whole. It encompasses the diversity of species, genes, and ecosystems, and is crucial for the functioning and stability of ecosystems. Understanding what determines high biodiversity is essential for conservation efforts and sustainable management of natural resources.
Factors influencing high biodiversity
Several factors contribute to high biodiversity in an ecosystem. One of the key determinants is the availability of suitable habitats. Different species have specific habitat requirements, such as temperature, moisture, and vegetation type. Ecosystems with a wide range of habitats, such as tropical rainforests or coral reefs, tend to have high biodiversity due to the presence of diverse niches that can support a variety of species.
Another factor that influences biodiversity is the size of the ecosystem. Larger ecosystems generally have higher biodiversity as they can support larger populations and a greater number of species. This is because larger areas provide more resources and reduce the risk of extinction due to natural disasters or human activities.
Additionally, the stability of an ecosystem plays a crucial role in determining its biodiversity. Ecosystems that experience minimal disturbances, such as natural disasters or human interference, are more likely to have high biodiversity. This is because stable environments allow species to thrive and evolve over time.
Furthermore, the presence of keystone species can significantly impact biodiversity. Keystone species are those that have a disproportionate effect on the structure and function of an ecosystem. Their presence or absence can influence the abundance and diversity of other species. For example, the loss of a keystone predator can lead to an increase in prey species, which can then impact other trophic levels and disrupt the balance of the ecosystem.
High biodiversity is determined by a combination of factors, including habitat availability, ecosystem size, stability, and the presence of keystone species. Understanding these factors is crucial for conservation efforts and the preservation of Earth’s rich biodiversity.
What is high or low biodiversity?
High biodiversity means that a region supports a wide variety of species, while low biodiversity implies that an area supports only a few. The reasons for variances in biodiversity are complex, but they include both natural and man-made causes.
High biodiversity refers to an ecosystem that contains a wide variety of different species. It is a measure of the number of different species present in a particular area. High biodiversity indicates a healthy and thriving ecosystem, as it suggests that there is a balance between different species and their interactions. High biodiversity is often associated with areas that have a wide range of habitats and environmental conditions, as this allows for the coexistence of many different species.
There are several benefits to having high biodiversity. Firstly, it increases the resilience of an ecosystem to environmental changes. With a greater number of species, there is a higher chance that some will be able to adapt and survive in changing conditions. This helps to maintain the overall stability and functioning of the ecosystem. Additionally, high biodiversity can provide important ecosystem services, such as pollination, nutrient cycling, and pest control. These services are crucial for human well-being and agricultural productivity.
Low biodiversity, on the other hand, refers to an ecosystem that has a limited number of different species. This can occur due to various factors, such as habitat destruction, pollution, or the introduction of invasive species. Low biodiversity is often associated with degraded or disturbed ecosystems, as it indicates a loss of species and a disruption of ecological processes.
Low biodiversity can have negative impacts on the functioning of an ecosystem. With fewer species, there is a reduced capacity for the ecosystem to provide important services and support human livelihoods. For example, a decrease in pollinator species can lead to a decline in crop yields. Additionally, low biodiversity can make ecosystems more vulnerable to disturbances, such as disease outbreaks or climate change. This is because there are fewer species available to fulfill different ecological roles and provide resilience.
In conclusion, high biodiversity is indicative of a healthy and functioning ecosystem, while low biodiversity suggests a loss of species and ecological disruption. Understanding and conserving biodiversity is crucial for maintaining the stability and resilience of ecosystems, as well as for supporting human well-being.
What is 3 example of biodiversity?
The three types of biodiversity are: Species Diversity. Genetic Diversity. Ecological Diversity.
Biodiversity refers to the variety of life forms found on Earth, including plants, animals, and microorganisms. It encompasses the genetic, species, and ecosystem diversity that exists in different habitats and ecosystems. Biodiversity is crucial for the functioning of ecosystems and provides numerous benefits to humans, such as food, medicine, and clean water. In this article, we will explore three examples of biodiversity that highlight the incredible range of life on our planet.
1. Tropical Rainforests: Tropical rainforests are one of the most biodiverse ecosystems on Earth. They are home to a vast array of plant and animal species, many of which are found nowhere else. For example, the Amazon rainforest in South America is estimated to contain around 40,000 plant species, 3,000 fish species, and 1,300 bird species. This incredible diversity is due to the favorable climate and abundant resources found in these regions.
2. Coral Reefs: Coral reefs are another example of biodiversity hotspots. These underwater ecosystems are teeming with life, hosting a wide variety of fish, corals, and other marine organisms. Coral reefs are often referred to as the “”rainforests of the sea”” due to their high levels of biodiversity. They provide habitat for countless species and are essential for the health of marine ecosystems.
3. African Savannas: African savannas are vast grassland ecosystems that support a diverse range of plant and animal species. These ecosystems are characterized by a mix of grasses and scattered trees, providing habitat for large herbivores like elephants, giraffes, and zebras, as well as predators like lions and cheetahs. The African savannas are not only home to iconic wildlife but also play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of nature.
These examples illustrate the incredible diversity of life on Earth and the importance of preserving biodiversity. However, biodiversity is currently under threat due to human activities such as deforestation, pollution, and climate change. It is essential that we take action to protect and conserve biodiversity to ensure the continued existence of these unique ecosystems and the benefits they provide to both humans and the planet as a whole.
Is high biodiversity good for the environment?
Biodiversity is essential for the processes that support all life on Earth, including humans. Without a wide range of animals, plants and microorganisms, we cannot have the healthy ecosystems that we rely on to provide us with the air we breathe and the food we eat. And people also value nature of itself.
Biodiversity refers to the variety of life forms present in a particular ecosystem. It encompasses the diversity of species, genes, and ecosystems. High biodiversity is often considered beneficial for the environment due to several reasons. Firstly, it ensures the stability and resilience of ecosystems. A diverse range of species provides a buffer against disturbances such as climate change, disease outbreaks, and habitat destruction. This is because different species have different ecological roles and adaptations, allowing them to respond differently to environmental changes. Therefore, high biodiversity increases the chances of some species being able to survive and thrive even in the face of adversity.
Secondly, high biodiversity promotes ecosystem functioning. Each species in an ecosystem plays a unique role in maintaining the balance and functioning of the ecosystem. For example, plants are responsible for oxygen production and carbon sequestration, while insects and birds are important for pollination and seed dispersal. When there is a high diversity of species, these ecological processes are more efficient and effective, leading to healthier and more productive ecosystems.
Furthermore, high biodiversity contributes to the provision of ecosystem services. Ecosystem services are the benefits that humans derive from nature, such as clean air and water, food, and medicine. A diverse range of species ensures the availability and sustainability of these services. For instance, diverse plant communities help in soil fertility and nutrient cycling, which are essential for agriculture. Additionally, many pharmaceutical drugs are derived from natural sources, and rich biodiversity increases the chances of discovering new medicinal compounds.
In conclusion, high biodiversity is indeed good for the environment. It ensures the stability and resilience of ecosystems, promotes ecosystem functioning, and contributes to the provision of ecosystem services. Therefore, it is crucial to protect and conserve biodiversity to maintain the health and well-being of both the environment and human society.
How is high biodiversity defined?
High biodiversity is defined as the presence of a wide variety of different species within a given ecosystem or region. It refers to the number of different species, as well as the abundance and distribution of those species. Biodiversity can be measured at different levels, including genetic diversity, species diversity, and ecosystem diversity. Genetic diversity refers to the variety of genes within a species, while species diversity refers to the number of different species present in an area. Ecosystem diversity refers to the variety of different ecosystems or habitats within a region.
High biodiversity is often characterized by a rich and complex web of interactions between different species and their environment. It is a measure of the health and resilience of an ecosystem, as well as its ability to provide important ecological services, such as nutrient cycling, pollination, and pest control. Biodiversity is influenced by a range of factors, including climate, habitat availability, and human activities. Understanding and conserving high biodiversity is crucial for maintaining the balance and functioning of ecosystems, as well as for the well-being of human societies.
What factors contribute to high biodiversity?
There are several factors that contribute to high biodiversity in an ecosystem. One of the main factors is the availability of different habitats and niches. When an ecosystem has a variety of habitats such as forests, wetlands, grasslands, and coral reefs, it provides a wide range of living conditions for different species. This allows for the coexistence of a greater number of species with different ecological requirements.
Another factor that contributes to high biodiversity is the presence of a large number of different species within each habitat. This is known as species richness. When there are many different species present, it increases the overall biodiversity of the ecosystem. Additionally, the genetic diversity within each species also contributes to overall biodiversity. Genetic diversity allows species to adapt to changing environmental conditions and increases their chances of survival.
Why is high biodiversity important?
High biodiversity is important for several reasons. Firstly, it ensures the stability and resilience of ecosystems. A diverse range of species means that there are more options for adaptation and survival in the face of environmental changes. This is particularly crucial in the face of climate change, as species with different traits and abilities can help maintain ecosystem functions and services.
Secondly, high biodiversity is important for human well-being. Many of the resources we rely on, such as food, medicine, and clean water, are derived from natural ecosystems. A diverse range of species provides a greater potential for discovering new drugs and developing sustainable agricultural practices. Additionally, diverse ecosystems are more productive and can provide greater resilience to natural disasters, such as floods and droughts.
How does high biodiversity impact ecosystems?
High biodiversity has a profound impact on ecosystems, playing a crucial role in their stability and functioning. One of the key ways in which high biodiversity impacts ecosystems is through the provision of various ecosystem services. These services include the regulation of climate, water purification, pollination, and nutrient cycling. The presence of a diverse range of species ensures that these services are efficiently carried out, contributing to the overall health and resilience of ecosystems.
Furthermore, high biodiversity also enhances the productivity and productivity stability of ecosystems. Different species have unique ecological roles and functions, and their interactions within ecosystems create a complex web of relationships. This complexity increases the efficiency of energy and nutrient flow, leading to increased productivity. Additionally, high biodiversity can also enhance the resistance and resilience of ecosystems to disturbances such as climate change, disease outbreaks, and invasive species.
What are some examples of regions with high biodiversity?
There are several regions around the world that are known for their high biodiversity. One such example is the Amazon rainforest in South America. The Amazon is home to an incredible array of plant and animal species, many of which are found nowhere else on Earth. The sheer size and complexity of the rainforest, along with its favorable climate, make it a hotspot for biodiversity. The Amazon is often referred to as the “lungs of the Earth” due to its role in producing oxygen and regulating the global climate.
Another region with high biodiversity is the Coral Triangle, located in the western Pacific Ocean. This area, which includes parts of Indonesia, the Philippines, Malaysia, Papua New Guinea, and the Solomon Islands, is known for its rich coral reefs. These reefs support a vast array of marine life, including numerous species of fish, turtles, and corals. The Coral Triangle is considered the epicenter of marine biodiversity and is recognized as a global priority for conservation.
High biodiversity refers to the presence of a wide variety of different species in a given ecosystem or area. It is a measure of the richness and abundance of life forms, including plants, animals, and microorganisms, within a particular habitat. Biodiversity is often used as an indicator of the health and stability of an ecosystem, as well as its ability to provide essential services and support human well-being.
Conclusion
There are several factors that contribute to high biodiversity. One of the key factors is the availability of suitable habitats and resources for different species. A diverse range of habitats, such as forests, wetlands, grasslands, and coral reefs, can support a greater number of species with varying ecological requirements. Additionally, the presence of diverse vegetation types and structural complexity within habitats can provide niches and microhabitats for different organisms, further enhancing biodiversity.
Another important factor is the presence of ecological interactions and relationships between species. Biodiversity is often higher in areas where there are complex food webs, symbiotic relationships, and interactions such as predation, competition, and mutualism. These interactions contribute to the stability and resilience of ecosystems, as well as the overall functioning of ecological processes.
High biodiversity is crucial for the functioning and sustainability of ecosystems. It provides a range of ecosystem services, including the provision of food, clean water, air purification, climate regulation, and nutrient cycling. Biodiversity also plays a vital role in supporting human well-being, as it contributes to cultural, aesthetic, and recreational values. Additionally, high biodiversity can enhance the resilience of ecosystems to environmental changes and disturbances, such as climate change and habitat loss.
However, high biodiversity is under threat due to various human activities, including habitat destruction, pollution, overexploitation of resources, and climate change. These activities can lead to the loss of species and habitats, resulting in a decline in biodiversity. It is essential to recognize the value of biodiversity and take proactive measures to conserve and protect it for the benefit of present and future generations.



