Why Is Biodiversity Important To Ecosystems
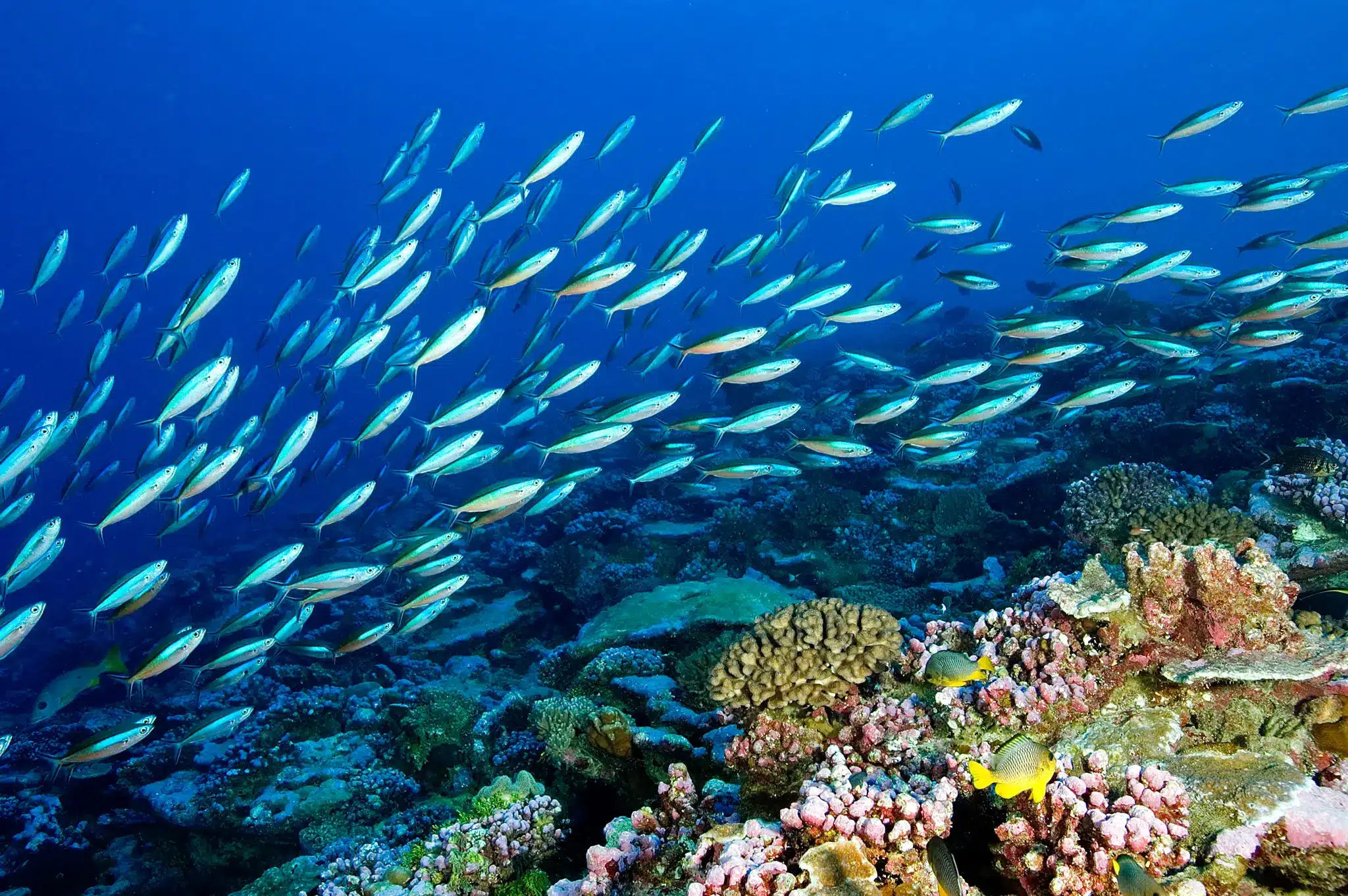

Biodiversity refers to the variety of life forms found in a particular ecosystem or on the entire planet. It encompasses the diversity of species, genes, and ecosystems, and is crucial for the functioning and stability of ecosystems. Biodiversity is not only important for the survival of different species but also for the well-being of human beings. It provides numerous ecosystem services that are essential for our survival and quality of life.
First and foremost, biodiversity plays a key role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems. Each species has a unique role to play in the web of life, and the loss of even a single species can have far-reaching consequences. For example, predators help control the population of prey species, while pollinators are essential for the reproduction of many plants. When biodiversity is reduced, these ecological interactions are disrupted, leading to imbalances and potential collapse of ecosystems.
Furthermore, biodiversity is crucial for the resilience and adaptability of ecosystems in the face of environmental changes. Ecosystems with high biodiversity are better able to withstand disturbances such as climate change, pollution, and invasive species. This is because diverse ecosystems have a greater range of genetic variation, which allows them to adapt and recover more effectively. In contrast, ecosystems with low biodiversity are more vulnerable to these disturbances, making them more prone to degradation and loss of functionality.
In addition to its ecological importance, biodiversity also provides numerous benefits to human societies. Many of our basic needs, such as food, medicine, and clean water, are directly or indirectly derived from biodiversity. For example, a wide variety of crops and livestock species are essential for global food security. Furthermore, many pharmaceutical drugs are derived from natural compounds found in plants and animals. Biodiversity also contributes to cultural and recreational values, as it provides inspiration for art, music, and tourism.
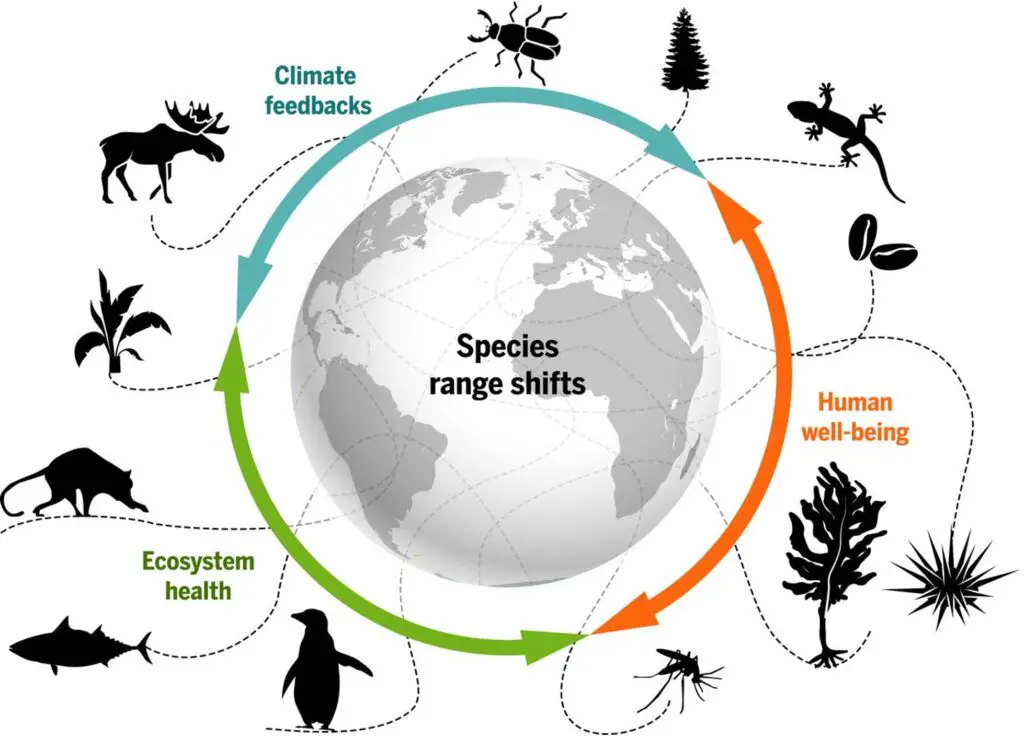
Why is biodiversity important to ecosystems choose the best answer?
Ecological life support—biodiversity provides functioning ecosystems that supply oxygen, clean air and water, pollination of plants, pest control, wastewater treatment and many ecosystem services.
Biodiversity is the variety of life on Earth, including the different species of plants, animals, and microorganisms, as well as the genetic diversity within each species. It is a fundamental aspect of ecosystems and plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance and functioning of these systems. Biodiversity is important to ecosystems for several reasons, and understanding its significance is essential for the conservation and sustainable management of our planet’s natural resources.
Firstly, biodiversity is important for the stability and resilience of ecosystems. A diverse range of species within an ecosystem ensures that there are multiple interactions and relationships between organisms. This interconnectedness helps to maintain the overall health and functioning of the ecosystem. For example, a diverse community of plants can provide a variety of food sources and habitats for different animals, which in turn helps to regulate populations and control pests.
Secondly, biodiversity is crucial for the provision of ecosystem services. Ecosystem services are the benefits that humans derive from nature, such as clean air and water, pollination of crops, and regulation of climate. A diverse range of species is necessary for the proper functioning of these services. For instance, bees and other pollinators are essential for the reproduction of many plants, including those that provide us with food. Without a diverse range of pollinators, our agricultural systems would be severely impacted.
Thirdly, biodiversity contributes to the resilience of ecosystems in the face of environmental changes. As the climate changes and habitats are altered, species with different traits and adaptations may be better suited to survive and thrive in these new conditions. A diverse range of species increases the likelihood that some will be able to adapt and persist, ensuring the long-term survival of the ecosystem.
Lastly, biodiversity has intrinsic value and is important for cultural and aesthetic reasons. Many people derive enjoyment and inspiration from the natural world, and the diversity of life forms is a source of wonder and beauty. Preserving biodiversity allows future generations to experience and appreciate the richness of our planet’s ecosystems.
What are 5 reasons why biodiversity is important?
Organisms, ecosystems and ecological processes supply us with oxygen and clean water, they help cycle carbon and fix nutrients, they enable plants to grow, they keep pests and diseases in check, and they help protect against flooding and to regulate the climate.
Biodiversity refers to the variety of life forms on Earth, including plants, animals, and microorganisms. It encompasses the genetic, species, and ecosystem diversity that exists in different habitats and ecosystems. Biodiversity is crucial for the functioning of ecosystems and provides numerous benefits to human society. Here are five reasons why biodiversity is important:
1. Ecosystem stability: Biodiversity plays a vital role in maintaining the stability and resilience of ecosystems. Each species within an ecosystem has a specific role or function, and the interactions between different species help to regulate ecological processes such as nutrient cycling, pollination, and pest control. A diverse ecosystem is more resilient to disturbances, such as climate change or natural disasters, as it can better adapt and recover.
2. Economic value: Biodiversity is a valuable economic resource. Many industries rely on biodiversity for raw materials, such as timber, fibers, and medicinal plants. Additionally, biodiversity supports ecotourism, which generates revenue and employment opportunities. Protecting and conserving biodiversity can contribute to sustainable economic development.
3. Food security: Biodiversity is essential for food production and agricultural systems. A diverse range of crops, livestock, and aquatic species provide a variety of food sources, nutrients, and genetic resources. Genetic diversity within crops and livestock is crucial for breeding programs to develop new varieties that are resistant to pests, diseases, and environmental stresses. Preserving biodiversity in agricultural landscapes is vital for ensuring long-term food security.
4. Medicinal resources: Biodiversity is a rich source of medicinal resources. Many plants, animals, and microorganisms contain compounds that have been used for centuries in traditional medicine and are now being investigated for their potential in modern medicine. Protecting biodiversity is crucial for preserving these valuable resources and discovering new drugs and treatments.
5. Cultural and aesthetic value: Biodiversity is deeply intertwined with human culture and provides aesthetic and recreational value. Many cultures have traditional practices, rituals, and beliefs that are closely connected to the natural world. Biodiversity also enhances the beauty of landscapes and provides opportunities for outdoor activities such as hiking, birdwatching, and photography.
Why is biodiversity important to an ecosystem quizlet?
Biodiversity is the variety of life in the world or in a particular habitat or ecosystem. Biodiversity is important because it provides us with Natural Resources (Food, Water, Wood, etc.) Natural Services (Pest Control, Air and Water Purification, etc.) and of course, Aesthetic Pleasure.
Biodiversity refers to the variety of living organisms in a particular area, including plants, animals, and microorganisms. It is a measure of the health and resilience of an ecosystem. Biodiversity is important to an ecosystem for several reasons, as it provides numerous benefits and services that are essential for the survival and well-being of all living organisms.
Firstly, biodiversity plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems. Each species within an ecosystem has a specific role or niche, and the interactions between different species help to regulate populations and maintain the overall stability of the ecosystem. For example, predators help control the population of prey species, preventing them from becoming too abundant and causing imbalances in the food chain.
Secondly, biodiversity is important for the provision of ecosystem services. Ecosystem services are the benefits that humans derive from ecosystems, such as clean air and water, pollination of crops, and the regulation of climate. A diverse range of species is necessary to ensure the functioning of these services. For instance, bees and other pollinators are essential for the reproduction of many plants, including those that provide us with food.
Thirdly, biodiversity contributes to the resilience of ecosystems in the face of environmental changes and disturbances. A diverse ecosystem is better able to adapt and recover from disturbances such as natural disasters or climate change. This is because different species have different tolerances and responses to environmental conditions, so if one species is negatively affected, others may be able to compensate and maintain the overall functioning of the ecosystem.
Furthermore, biodiversity has intrinsic value and is important for cultural and aesthetic reasons. Many people derive enjoyment and inspiration from the beauty and diversity of nature. Additionally, biodiversity is often closely tied to cultural practices and traditions, and the loss of certain species or habitats can have significant cultural impacts.
Biodiversity is crucial to the functioning and well-being of ecosystems. It provides a range of benefits and services that are essential for the survival of all living organisms, including humans. Protecting and conserving biodiversity is therefore of utmost importance to ensure the long-term sustainability of our planet.
How is biodiversity related to ecosystem?
Biodiversity is fundamental to sustaining life, supplying critical ecosystem services such as food provisioning, water purification, flood and drought control, nutrient cycling, and climate regulation. These services are essential to support human well-being and economic growth.
Biodiversity refers to the variety of living organisms present in a particular ecosystem. It encompasses the different species of plants, animals, and microorganisms, as well as the genetic diversity within each species. Ecosystem, on the other hand, refers to the interactions between living organisms and their physical environment. It includes the biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) components of a particular area.
Biodiversity and ecosystem are closely interconnected and dependent on each other. The presence of a diverse range of species within an ecosystem is crucial for its stability and functioning. Each species plays a unique role in maintaining the balance of the ecosystem. For example, plants are responsible for producing oxygen through photosynthesis, which is essential for the survival of other organisms. Animals, on the other hand, help in pollination, seed dispersal, and nutrient cycling.
Biodiversity also contributes to the resilience of ecosystems. A diverse ecosystem is better able to withstand and recover from disturbances such as natural disasters or climate change. This is because different species have different adaptations and abilities to cope with changes in their environment. If an ecosystem has low biodiversity, it becomes more vulnerable to disruptions and may struggle to recover.
Furthermore, biodiversity provides numerous ecosystem services that are essential for human well-being. These services include the provision of food, clean water, air purification, and climate regulation. For example, forests with high biodiversity act as carbon sinks, helping to mitigate climate change by absorbing and storing carbon dioxide. Biodiversity also plays a crucial role in the development of medicines, as many pharmaceutical drugs are derived from natural sources.
However, human activities such as deforestation, pollution, and habitat destruction are causing a rapid loss of biodiversity. This loss not only threatens the survival of many species but also disrupts the functioning of ecosystems. It is important to recognize the value of biodiversity and take steps to conserve and protect it for the benefit of both ecosystems and human society.
What are the 3 major importance of biodiversity?
Why is biodiversity important? Biodiversity is essential for human health and well-being, economic prosperity, food safety, and security, and other areas critical to all humans and all human societies.
Biodiversity refers to the variety of life forms found on Earth, including plants, animals, and microorganisms. It encompasses the genetic, species, and ecosystem diversity that exists in different habitats and ecosystems. Biodiversity is crucial for the functioning of ecosystems and provides numerous benefits to human society. There are three major importance of biodiversity that highlight its significance in maintaining the balance of nature and supporting human well-being.
Firstly, biodiversity plays a vital role in maintaining the stability and resilience of ecosystems. Ecosystems are complex networks of interactions between different species and their environment. The presence of a diverse range of species ensures that ecosystems can withstand and recover from disturbances such as natural disasters or climate change. Each species has a unique role to play in the ecosystem, and the loss of even a single species can have cascading effects on the entire ecosystem.
Secondly, biodiversity is essential for the provision of ecosystem services. Ecosystem services are the benefits that humans derive from nature, including the provision of food, clean water, air purification, and climate regulation. Biodiversity is directly linked to the functioning of these services. For example, diverse plant species contribute to the pollination of crops, which is essential for agricultural productivity. Similarly, forests with high biodiversity are more effective in sequestering carbon dioxide and mitigating climate change.
Lastly, biodiversity has intrinsic value and is a source of inspiration and cultural significance. Each species has its own unique characteristics and contributes to the beauty and wonder of the natural world. Biodiversity also plays a crucial role in cultural practices and traditions of indigenous communities. Many cultures have deep connections with specific species or ecosystems, and the loss of biodiversity can result in the erosion of cultural heritage.
Biodiversity is of utmost importance for the functioning of ecosystems, the provision of ecosystem services, and the preservation of cultural and aesthetic values. It is essential to recognize and protect biodiversity to ensure the well-being of both nature and human society.
What role does biodiversity play in maintaining the balance of ecosystems?
Biodiversity plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems. It refers to the variety of species, genes, and ecosystems present in a given area. A diverse ecosystem is more resilient and able to withstand disturbances such as climate change, disease outbreaks, and habitat loss. This is because different species have different roles and functions within an ecosystem, and their interactions help to maintain the overall balance.
For example, a diverse plant community can provide a range of resources such as food, shelter, and nesting sites for different animal species. This interdependence ensures that the ecosystem remains stable and functional. Additionally, biodiversity also contributes to the cycling of nutrients, the purification of air and water, and the regulation of climate, all of which are essential for the health and functioning of ecosystems.
How does biodiversity contribute to the overall health and resilience of ecosystems?
Biodiversity plays a crucial role in maintaining the overall health and resilience of ecosystems. Firstly, a diverse range of species within an ecosystem ensures that there are multiple interactions and relationships between different organisms. This interconnectedness allows for the efficient cycling of nutrients, energy flow, and the maintenance of ecological processes. Each species has its own unique role and function, and the presence of a variety of species ensures that these functions are fulfilled.
Furthermore, biodiversity provides a form of insurance for ecosystems. In the face of environmental changes or disturbances, such as climate change or natural disasters, a diverse ecosystem is more likely to have species that can adapt and survive. This resilience is crucial for the long-term survival and stability of ecosystems. Additionally, a diverse ecosystem is better equipped to resist the spread of diseases and pests. The presence of different species with varying levels of susceptibility to diseases reduces the risk of widespread outbreaks.
In what ways does biodiversity support the functioning of various ecological processes within ecosystems?
Biodiversity plays a crucial role in supporting the functioning of various ecological processes within ecosystems. One way it does this is through the process of nutrient cycling. Different species within an ecosystem have different roles in breaking down organic matter and recycling nutrients back into the soil. This helps to maintain the fertility of the soil and ensures that essential nutrients are available for plants to grow. Without a diverse range of species carrying out these processes, nutrient cycling would be disrupted, leading to imbalances in the ecosystem.
Another important ecological process that biodiversity supports is pollination. Many plants rely on animals, such as bees and butterflies, to transfer pollen between flowers, enabling them to reproduce. This process is essential for the production of fruits and seeds, which not only sustains plant populations but also provides food for other animals. Without a diverse range of pollinators, many plant species would struggle to reproduce, leading to a decline in their populations and potentially impacting the entire ecosystem.
Can you explain the relationship between biodiversity and the stability of ecosystems?
Biodiversity is closely linked to the stability of ecosystems. A diverse ecosystem is more resilient and better able to withstand disturbances, such as natural disasters or human activities. This is because a diverse ecosystem contains a variety of species with different traits and functions, which allows for a greater range of responses to changing conditions. For example, if a particular species is unable to adapt to a new environmental stressor, other species may be able to fill the ecological niche and maintain the overall functioning of the ecosystem.
Furthermore, biodiversity provides a form of insurance against environmental changes. In a diverse ecosystem, there is a higher likelihood that at least some species will be able to survive and reproduce under changing conditions. This ensures the continued provision of ecosystem services, such as nutrient cycling, pollination, and pest control. In contrast, a less diverse ecosystem is more vulnerable to disruptions, as it may rely heavily on a few key species. If these species are lost or their populations decline, the stability and functioning of the ecosystem can be severely compromised.
What are some specific examples of how biodiversity directly benefits ecosystems and the services they provide?
Biodiversity directly benefits ecosystems and the services they provide in numerous ways. One example is through pollination. Many plants rely on pollinators such as bees, butterflies, and birds to transfer pollen between flowers, enabling them to reproduce. Without a diverse range of pollinators, the reproduction of these plants would be severely limited, leading to a decline in plant populations and a loss of ecosystem services such as food production and habitat provision.
Another example is nutrient cycling. Biodiversity plays a crucial role in breaking down organic matter and recycling nutrients within ecosystems. Different species of decomposers, such as bacteria, fungi, and insects, contribute to the decomposition process by breaking down dead plant and animal material. This decomposition releases nutrients back into the soil, making them available for uptake by plants. Without a diverse range of decomposers, nutrient cycling would be disrupted, leading to nutrient-poor soils and reduced plant growth.
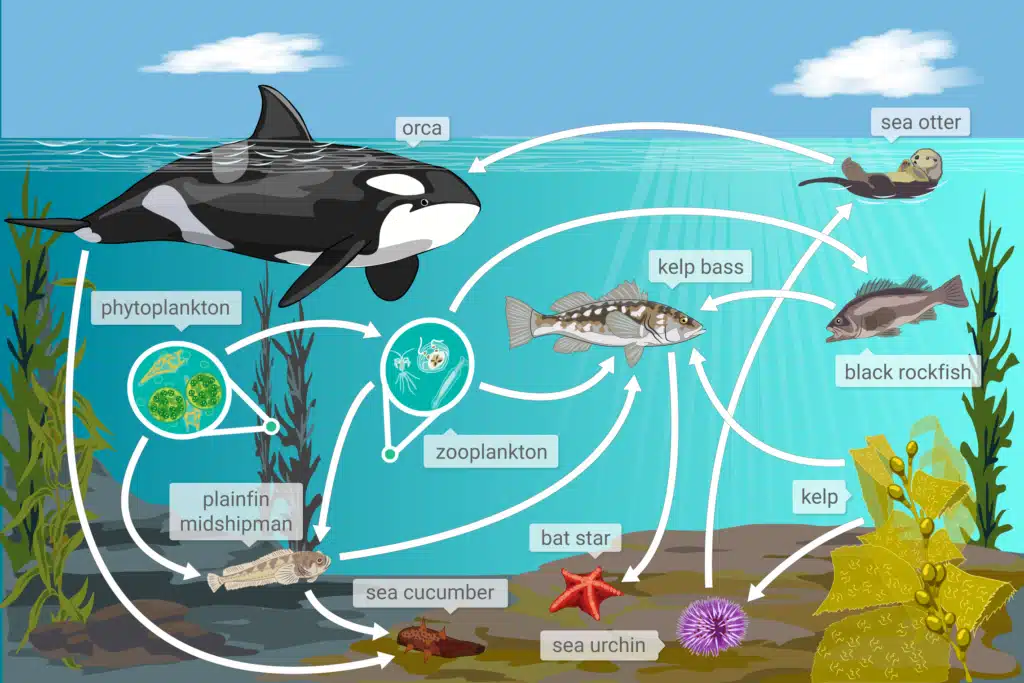
Conclusion
Biodiversity refers to the variety of living organisms in a particular habitat or ecosystem. It encompasses the diversity of species, genes, and ecosystems, and plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance and functioning of ecosystems. Biodiversity is important to ecosystems for several reasons, as it provides numerous benefits and services that are essential for the survival and well-being of both humans and other species.
Firstly, biodiversity is important for the stability and resilience of ecosystems. A diverse range of species within an ecosystem ensures that there are multiple interactions and relationships between different organisms. This interconnectedness helps to maintain the overall health and functioning of the ecosystem. For example, a diverse community of plants can provide a variety of food sources and habitats for different animals, which in turn helps to regulate populations and control pests. Additionally, a diverse range of species can also enhance the ability of ecosystems to withstand and recover from disturbances such as natural disasters or climate change.
Secondly, biodiversity is crucial for the provision of ecosystem services. Ecosystem services are the benefits that humans derive from ecosystems, such as clean air and water, pollination of crops, and regulation of climate. Biodiversity plays a key role in providing these services. For instance, diverse plant communities contribute to the purification of air and water by absorbing pollutants and filtering out impurities. Similarly, diverse insect populations, including bees and butterflies, are important pollinators of many crops, ensuring food production. Furthermore, diverse ecosystems, such as forests and wetlands, help to regulate climate by sequestering carbon dioxide and mitigating the impacts of climate change.
Lastly, biodiversity has intrinsic value and is important for cultural and aesthetic reasons. Each species has its own unique characteristics and contributes to the overall beauty and diversity of the natural world. Biodiversity also holds cultural significance for many indigenous communities, who rely on traditional knowledge and practices that are closely tied to the natural environment. Preserving biodiversity is therefore not only important for the functioning of ecosystems and the provision of ecosystem services, but also for the preservation of cultural heritage and the enjoyment of future generations.
Discover the significance of biodiversity to ecosystems and understand why it plays a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of our natural world. Explore the interconnectedness of species and the benefits they bring to our environment.



