How Does Biodiversity Contribute To The Sustainability Of An Ecosystem

Introduction
How Does Biodiversity Contribute To The Sustainability Of An Ecosystem: Biodiversity refers to the variety of living organisms present in a particular ecosystem. It encompasses the diversity of species, genes, and ecosystems within a given area. Biodiversity is crucial for the sustainability of an ecosystem as it plays a vital role in maintaining the balance and functioning of natural systems. It is the foundation of all life on Earth and provides numerous benefits to humans and the environment.
Firstly, biodiversity contributes to the sustainability of an ecosystem by enhancing its resilience and stability. A diverse ecosystem is better able to withstand and recover from disturbances such as natural disasters, climate change, and disease outbreaks. This is because different species have different ecological roles and functions, and their interactions create a complex web of relationships that ensure the overall health and functioning of the ecosystem. For example, a diverse forest ecosystem with a variety of tree species is more resistant to pests and diseases, as compared to a monoculture plantation.
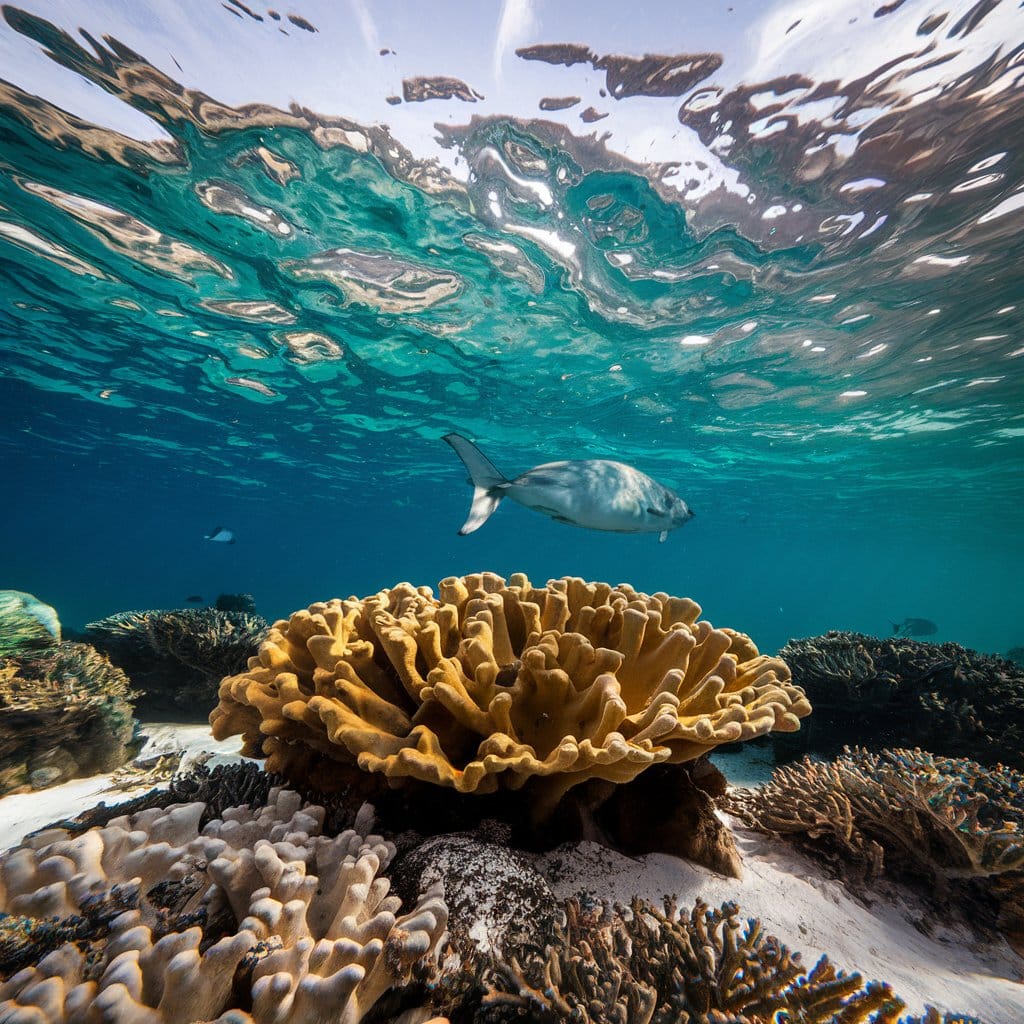
Secondly, biodiversity is essential for the provision of ecosystem services. Ecosystem services are the benefits that humans derive from nature, such as clean air and water, food, medicine, and climate regulation. A diverse ecosystem is more productive and efficient in providing these services. For instance, a diverse coral reef ecosystem supports a wide range of fish species, which in turn provide food and livelihoods for millions of people. Additionally, the presence of diverse plant species in an ecosystem enhances soil fertility, pollination, and pest control, leading to increased agricultural productivity.
Furthermore, biodiversity is crucial for the maintenance of genetic diversity within species. Genetic diversity is the variety of genes within a species and is essential for adaptation and evolution. A diverse gene pool allows species to adapt to changing environmental conditions, such as temperature fluctuations or the emergence of new diseases. This genetic variability ensures the long-term survival of species and their ability to respond to future challenges. Therefore, the conservation of biodiversity is vital for preserving the genetic resources that can be used for crop improvement, disease resistance, and other beneficial traits.
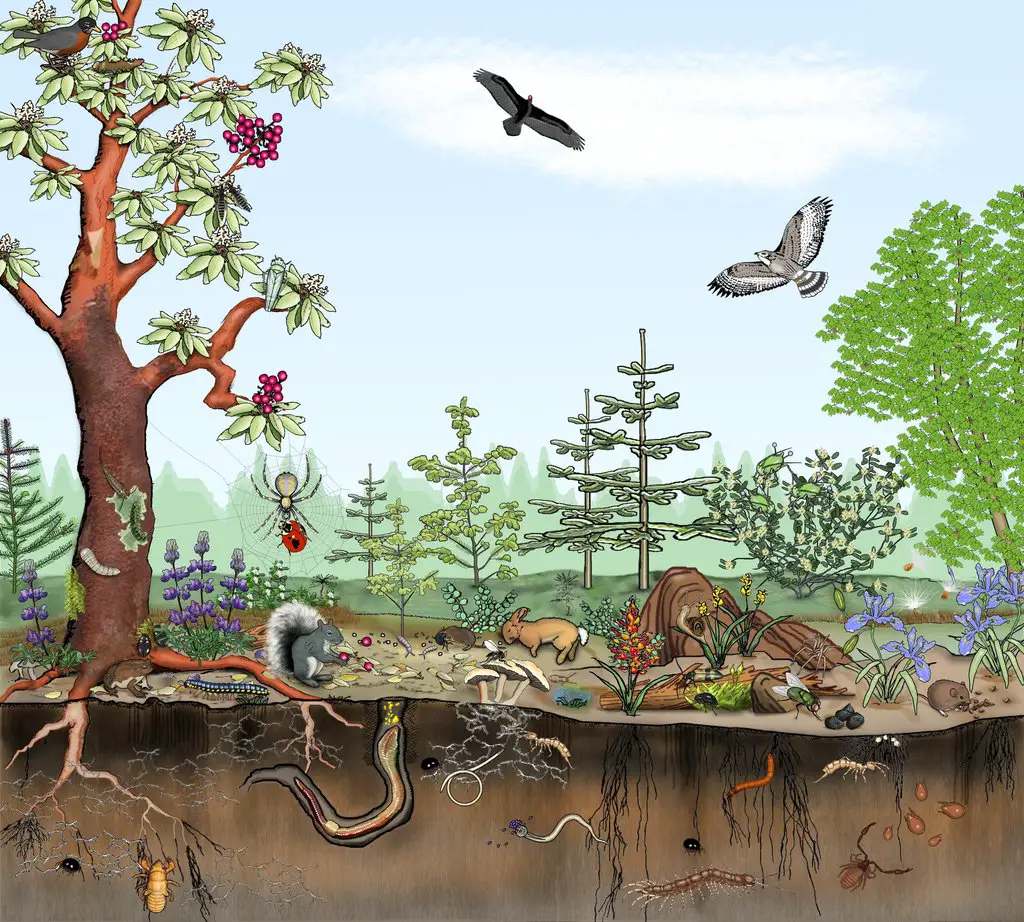

Why does biodiversity contribute to the sustainability of an ecosystem quizlet?
Why does biodiversity contribute to a habitat’s sustainability? The more plants and animals in a habitat, the greater the biomass, which is how habitats store energy. The greater the number of species, the more competition there is for food between predators, which sustains their populations.
Biodiversity refers to the variety of living organisms in a particular ecosystem. It encompasses the diversity of species, genes, and ecosystems within a given area. Biodiversity is crucial for the sustainability of an ecosystem as it plays a vital role in maintaining the balance and functioning of the natural world. It provides numerous benefits to both the environment and human society.
Firstly, biodiversity contributes to the sustainability of an ecosystem by enhancing its resilience and stability. A diverse ecosystem is better able to withstand and recover from disturbances such as natural disasters, climate change, and disease outbreaks. This is because different species have different ecological roles and adaptations, which allows them to respond differently to environmental changes. Therefore, if one species is negatively affected by a disturbance, others may be able to compensate for its loss and maintain the overall functioning of the ecosystem.
Secondly, biodiversity is essential for the provision of ecosystem services. Ecosystem services are the benefits that humans derive from the natural environment. These include the provision of food, clean water, air purification, climate regulation, and the regulation of pests and diseases. A diverse ecosystem is more likely to provide a wide range of ecosystem services, as different species contribute to different services. For example, pollinators such as bees and butterflies are crucial for the pollination of crops, which is essential for food production.
Furthermore, biodiversity is important for the maintenance of genetic diversity within species. Genetic diversity refers to the variety of genes within a species. It is crucial for the adaptation and survival of species in changing environments. A diverse gene pool allows for greater genetic variation, which increases the chances of a species being able to adapt to new conditions. This is particularly important in the face of climate change, as species will need to adapt to new temperature and precipitation patterns.
Biodiversity is a fundamental component of a sustainable ecosystem. It enhances the resilience and stability of ecosystems, provides essential ecosystem services, and maintains genetic diversity within species. Therefore, it is crucial to protect and conserve biodiversity to ensure the long-term sustainability of our ecosystems and the well-being of both the environment and human society.
Which is an example of biodiversity contributing to the sustainability?
Biodiversity’s direct contributions to sustainable development are numerous and wide-ranging. For example, a diversity of pollinators ensures crop pollination, and a third of global food production is dependent on them (which links clearly to SDG2).
Biodiversity refers to the variety of life forms, including plants, animals, and microorganisms, that exist on Earth. It is a crucial component of the planet’s ecosystems and plays a significant role in maintaining the sustainability of our environment. Biodiversity contributes to sustainability in various ways, and one example of this is the role it plays in supporting ecosystem services.
Ecosystem services are the benefits that humans derive from ecosystems. These services include the provision of food, clean water, air purification, climate regulation, and the regulation of diseases. Biodiversity is essential for the functioning of these services. For example, a diverse range of plant species is necessary for the production of food crops. Different plant species have different characteristics, such as resistance to pests or tolerance to specific environmental conditions, which can help ensure food security in the face of changing climate conditions or disease outbreaks.
Biodiversity also contributes to the sustainability of ecosystems by enhancing their resilience and stability. Ecosystems with higher biodiversity are generally more resilient to disturbances, such as natural disasters or human activities. This is because a diverse range of species provides a greater variety of functions and interactions within an ecosystem, making it more adaptable to changes. For example, in a forest ecosystem, a diverse range of tree species can help prevent the spread of diseases or pests that may affect a single species.
Biodiversity also plays a crucial role in maintaining the health of ecosystems. Different species have different roles and functions within an ecosystem, and the loss of a single species can have cascading effects on the entire ecosystem. For example, the loss of a predator species can lead to an increase in the population of its prey, which can then have negative impacts on other species or disrupt the balance of the ecosystem. Therefore, maintaining biodiversity is essential for the long-term sustainability of ecosystems.
Biodiversity contributes to sustainability by supporting ecosystem services, enhancing the resilience of ecosystems, and maintaining their health. It is crucial to recognize the value of biodiversity and take steps to protect and conserve it for the benefit of present and future generations.
What are 5 reasons why biodiversity is important?
Organisms, ecosystems and ecological processes supply us with oxygen and clean water, they help cycle carbon and fix nutrients, they enable plants to grow, they keep pests and diseases in check, and they help protect against flooding and to regulate the climate.
Ecosystem Stability Biodiverse ecosystems are more resilient to disturbances and environmental changes. The presence of diverse species ensures that ecological functions, such as nutrient cycling, pollination, and pest control, remain balanced and efficient. This stability enhances the ecosystem’s ability to withstand and recover from natural disasters or human-induced impacts like climate change.
Human Health and Medicine Biodiversity provides a vast array of medicinal resources. Many plants, animals, and microorganisms contain compounds that have been used to develop life-saving drugs and treatments. Moreover, exposure to diverse ecosystems can positively impact human mental health, offering recreational and therapeutic benefits.
Food Security Biodiversity is the foundation of our food systems. A diverse range of crops, livestock, and aquatic species contribute to global food security by offering genetic resilience to diseases, pests, and changing climatic conditions. Maintaining biodiversity in agriculture also ensures sustainable practices and safeguards against potential food crises.
Economic Benefits Biodiversity supports economies through various industries, such as agriculture, forestry, fisheries, and tourism. These sectors rely on diverse natural resources and healthy ecosystems to generate income and employment opportunities, contributing significantly to national and global economies.
Cultural and Aesthetic Value Biodiversity enriches cultural heritage and spiritual connections. Indigenous and local communities often rely on nature for cultural practices, traditional knowledge, and spiritual beliefs. Additionally, the beauty and wonder of diverse landscapes and wildlife inspire artistic expression, offering aesthetic enjoyment and promoting environmental awareness.
What is an example of sustainability in ecosystem?
Healthy wetlands are a self-sufficient ecosystem and are the most productive ecosystem in the world. It provides protection to the ecosystem, improves the water quality, provides fish and wildlife habitats, and maintains surface water during dry seasons.
Sustainability in an ecosystem refers to the ability of the ecosystem to maintain its balance and functionality over time. It involves the conservation and efficient use of resources, as well as the preservation of biodiversity. An example of sustainability in an ecosystem can be seen in the Amazon rainforest.
The Amazon rainforest is the largest tropical rainforest in the world, covering an area of approximately 5.5 million square kilometers. It is home to a diverse range of plant and animal species, many of which are found nowhere else on Earth. The rainforest plays a crucial role in regulating the global climate, as it absorbs a significant amount of carbon dioxide and releases oxygen through photosynthesis.
One of the key factors contributing to the sustainability of the Amazon rainforest is the indigenous communities that have lived in harmony with the ecosystem for centuries. These communities have developed sustainable practices that allow them to utilize the resources of the rainforest without causing significant harm to the environment. For example, they practice selective logging, which involves carefully choosing which trees to cut down and leaving the rest to regenerate. This ensures that the forest can continue to provide resources for future generations.
Another example of sustainability in the Amazon rainforest is the conservation efforts undertaken by various organizations and governments. Protected areas have been established to safeguard the biodiversity of the rainforest, and measures have been put in place to prevent illegal logging and deforestation. These efforts aim to maintain the delicate balance of the ecosystem and ensure its long-term sustainability.
In addition, sustainable tourism has also played a role in promoting the sustainability of the Amazon rainforest. Eco-friendly lodges and tour operators have emerged, offering visitors the opportunity to experience the beauty of the rainforest while minimizing their impact on the environment. These initiatives provide economic incentives for the conservation of the rainforest and support the livelihoods of local communities.
What are 3 reasons why biodiversity is important in an ecosystem?
Why is biodiversity important? Biodiversity is essential for human health and well-being, economic prosperity, food safety and security, and other areas critical to all humans and all human societies.
Biodiversity refers to the variety of living organisms in a particular ecosystem. It encompasses the different species of plants, animals, and microorganisms, as well as the genetic diversity within each species. Biodiversity is crucial for the functioning and stability of ecosystems, and it provides numerous benefits to both humans and the environment. There are several reasons why biodiversity is important in an ecosystem, and three of the most significant ones are discussed below.
Firstly, biodiversity plays a vital role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems. Each species within an ecosystem has a specific role or niche to fulfill, and their interactions with other species are essential for the overall functioning of the ecosystem. For example, predators help control the population of prey species, preventing them from overpopulating and causing imbalances in the food chain. Similarly, pollinators such as bees and butterflies are crucial for the reproduction of many plant species. If any species within an ecosystem becomes extinct or its population declines significantly, it can disrupt the delicate balance and lead to cascading effects throughout the ecosystem.
Secondly, biodiversity contributes to the resilience and adaptability of ecosystems. A diverse range of species ensures that an ecosystem is better equipped to withstand and recover from disturbances such as natural disasters, climate change, or disease outbreaks. This is because different species have different traits and adaptations that allow them to survive under varying conditions. For instance, in a forest ecosystem, the presence of a variety of tree species with different growth rates and tolerance to different soil types ensures that the forest can regenerate and recover after a disturbance like a wildfire or logging.
Thirdly, biodiversity provides numerous ecosystem services that are essential for human well-being. These services include the provision of food, clean water, air purification, climate regulation, and the maintenance of soil fertility. For example, diverse plant species in agricultural systems can enhance crop productivity, improve soil health, and reduce the need for chemical inputs. Biodiversity also has cultural and aesthetic values, as it contributes to the beauty and diversity of landscapes, and provides recreational opportunities for people.
What is the relationship between biodiversity and the sustainability of an ecosystem?
Biodiversity refers to the variety of species and ecosystems present in a given area. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the sustainability of an ecosystem. A diverse ecosystem is more resilient and adaptable to environmental changes, making it more likely to survive and thrive in the long term.
Firstly, biodiversity ensures that there is a wide range of species with different ecological roles and functions. This means that if one species is negatively affected by a disturbance or change in the environment, there are other species that can step in and fulfill that role. This redundancy helps to maintain the overall functioning and stability of the ecosystem.
Secondly, biodiversity enhances the availability of resources within an ecosystem. Different species have different resource requirements, and a diverse ecosystem can support a greater variety of resources. This ensures that there is enough food, shelter, and other essential resources for all species, reducing competition and promoting the overall health of the ecosystem.
How does the presence of diverse species contribute to the overall health and stability of an ecosystem?
The presence of diverse species plays a crucial role in maintaining the overall health and stability of an ecosystem. Firstly, diverse species provide a wide range of ecological functions and services. Each species has its own unique set of traits and behaviors, which allows them to occupy different niches within the ecosystem. This means that they perform different roles such as pollination, nutrient cycling, and pest control. The presence of multiple species performing these functions ensures that the ecosystem is able to withstand disturbances and maintain its balance.
Furthermore, diverse species contribute to the resilience of an ecosystem. When faced with environmental changes or disturbances, such as climate change or natural disasters, ecosystems with higher biodiversity are better able to adapt and recover. This is because different species have different tolerances and responses to these changes. Some species may be more resistant to certain stressors, while others may be more resilient in the face of others. The presence of diverse species increases the likelihood that at least some species will be able to survive and thrive in changing conditions, ensuring the long-term stability of the ecosystem.
In what ways does biodiversity enhance the resilience and adaptability of an ecosystem?
Biodiversity plays a crucial role in enhancing the resilience and adaptability of an ecosystem. Firstly, a diverse range of species within an ecosystem ensures that there are multiple pathways for energy and nutrient flow. This redundancy in ecological functions allows for the ecosystem to withstand disturbances such as natural disasters or climate change. If one species is negatively affected by a disturbance, others can step in and fulfill its ecological role, maintaining the overall functioning of the ecosystem.
Furthermore, biodiversity increases the genetic diversity within a population, which is essential for the adaptability of species. Genetic diversity provides the raw material for natural selection to act upon, allowing species to evolve and adapt to changing environmental conditions. This genetic variation increases the chances of some individuals having traits that are advantageous in a changing environment, ensuring the survival and persistence of the species.
Can you explain the specific mechanisms through which biodiversity supports the functioning and productivity of an ecosystem?
Biodiversity plays a crucial role in supporting the functioning and productivity of an ecosystem through various mechanisms. One important mechanism is the concept of species complementarity. This refers to the idea that different species within an ecosystem have unique traits and functions, allowing them to utilize resources in different ways. This diversity of traits and functions ensures that resources are efficiently utilized and prevents the dominance of a single species. For example, in a forest ecosystem, different tree species may have different root structures, allowing them to access different soil depths and extract nutrients more effectively.
Another mechanism is the role of biodiversity in nutrient cycling. Different species contribute to the cycling of nutrients in an ecosystem through processes such as decomposition, nutrient uptake, and nutrient release. For instance, decomposer organisms like fungi and bacteria break down organic matter, releasing nutrients back into the soil. These nutrients are then taken up by plants, which in turn support the growth of herbivores and other organisms higher up in the food chain. This cycling of nutrients ensures a continuous supply of essential elements for the functioning and productivity of the ecosystem.
Are there any examples or case studies that demonstrate the positive impact of biodiversity on the long-term sustainability of ecosystems?
Yes, there are numerous examples and case studies that highlight the positive impact of biodiversity on the long-term sustainability of ecosystems. One such example is the Yellowstone National Park in the United States. In the 1990s, the reintroduction of gray wolves into the park had a profound effect on the ecosystem. The presence of wolves led to a decrease in the population of elk, which in turn allowed for the recovery of vegetation such as willows and aspens. This recovery of vegetation had a cascading effect on other species, including beavers, birds, and fish, leading to increased biodiversity and overall ecosystem health.
Another example is the Great Barrier Reef in Australia. The coral reefs in this ecosystem support a wide variety of marine species, including fish, turtles, and sharks. The diversity of species within the reef provides important ecological functions such as nutrient cycling, habitat creation, and disease resistance. However, due to climate change and other human activities, the Great Barrier Reef is facing significant threats. The decline in biodiversity within the reef has resulted in reduced resilience and adaptability, making it more vulnerable to further degradation. This example highlights the importance of maintaining biodiversity for the long-term sustainability of ecosystems.
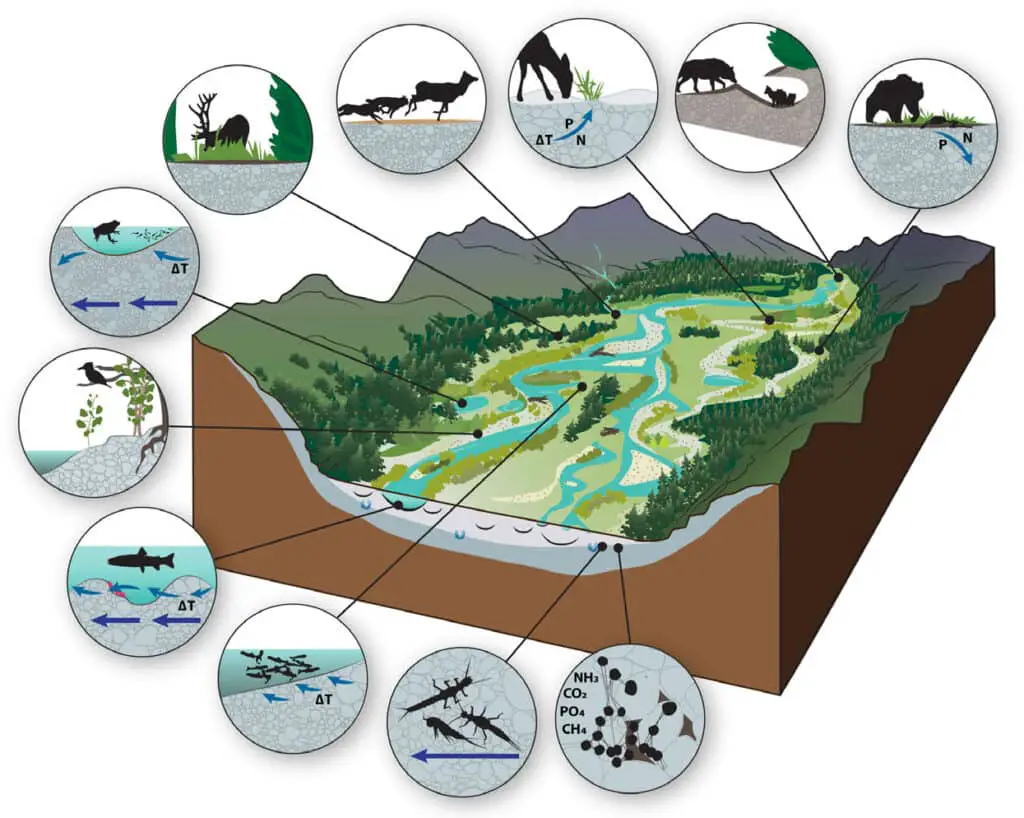
Conclusion
Biodiversity plays a crucial role in maintaining the sustainability of an ecosystem. It refers to the variety of living organisms, including plants, animals, and microorganisms, as well as the genetic diversity within each species. Biodiversity is essential for the functioning of ecosystems and provides numerous benefits to humans and the environment. In this essay, we will explore how biodiversity contributes to the sustainability of an ecosystem.
Firstly, biodiversity enhances the stability and resilience of ecosystems. A diverse range of species within an ecosystem ensures that there are multiple pathways for energy flow and nutrient cycling. This means that if one species is affected by a disturbance, such as a disease outbreak or a natural disaster, other species can step in and fulfill similar ecological roles. This redundancy in ecological functions helps to maintain the overall stability of the ecosystem and prevents the collapse of important ecological processes.
Secondly, biodiversity is crucial for the provision of ecosystem services. Ecosystem services are the benefits that humans derive from ecosystems, such as clean air and water, pollination of crops, and regulation of climate. A diverse range of species is necessary for the proper functioning of these services. For example, bees and other pollinators are essential for the reproduction of many plants, including food crops. Without a diverse range of pollinators, the productivity of agricultural systems would be severely impacted, leading to food shortages and economic losses.
Furthermore, biodiversity contributes to the resilience of ecosystems in the face of environmental changes. Climate change, habitat destruction, and pollution are some of the major threats to biodiversity. However, ecosystems with high biodiversity are often more resilient to these disturbances. This is because a diverse range of species provides a greater pool of genetic variation, which allows for adaptation to changing environmental conditions. Therefore, maintaining biodiversity is crucial for ensuring the long-term sustainability of ecosystems in the face of global environmental challenges.
Learn how biodiversity plays a crucial role in maintaining the long-term sustainability of ecosystems. Discover the various ways in which diverse species contribute to the overall health and resilience of our natural environment.



