What Are The Three Levels Of Biodiversity

Introduction
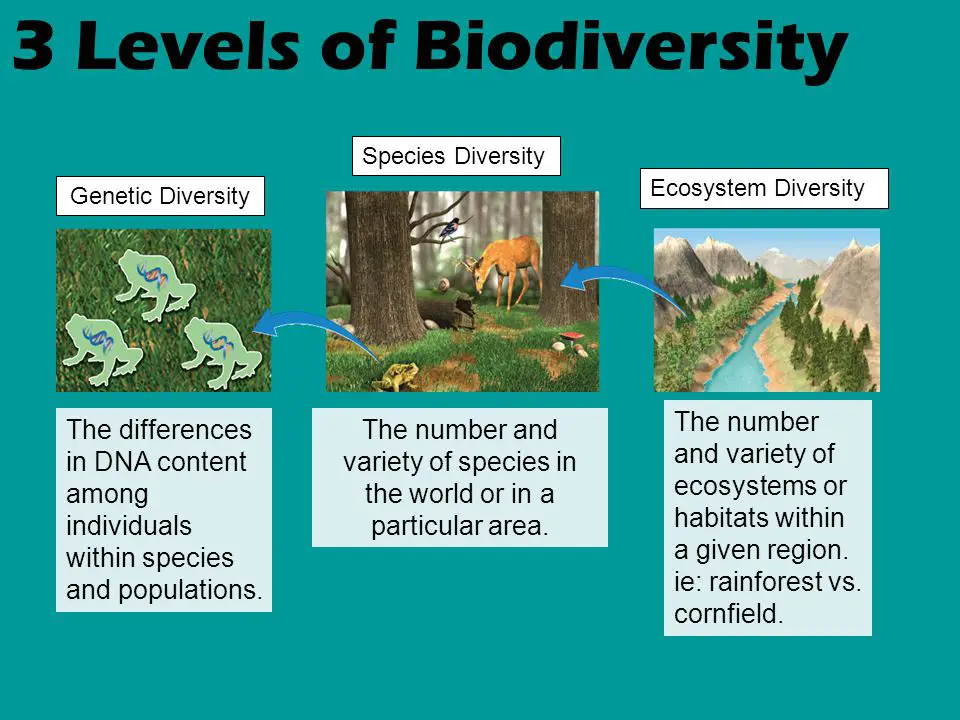
What Are The Three Levels Of Biodiversity: Biodiversity refers to the variety of life on Earth, including the diversity of species, genes, and ecosystems. It is a fundamental aspect of our planet’s health and plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems and supporting human well-being. Biodiversity can be categorized into three levels: genetic diversity, species diversity, and ecosystem diversity.Introduction What Are The Three Levels Of Biodiversity: Biodiversity refers to the variety of life on Earth, including the diversity of species, genes, and ecosystems. It is a fundamental aspect of our planet’s health and plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems and supporting human well-being. Biodiversity can be categorized into three levels: genetic diversity, species diversity, and ecosystem diversity.
Genetic diversity is the variation in genes within a species. It is the foundation of biodiversity and is essential for the survival and adaptation of species to changing environments. Genetic diversity allows species to evolve and develop traits that increase their chances of survival. It also provides the raw material for natural selection, enabling species to respond to environmental changes and threats such as diseases or climate change. Genetic diversity is crucial for maintaining the resilience and long-term viability of populations.
Species diversity refers to the variety of different species within a particular area or ecosystem. It encompasses the number of species present, as well as their relative abundance and distribution. Species diversity is a measure of the health and stability of an ecosystem. A high level of species diversity indicates a well-functioning ecosystem with a wide range of ecological niches and interactions. It also enhances ecosystem resilience, as different species may have different responses to disturbances or environmental changes. Species diversity is important for ecosystem services such as pollination, nutrient cycling, and pest control.
Ecosystem diversity is the variety of different ecosystems or habitats within a region or on a global scale. It includes terrestrial, freshwater, and marine ecosystems, as well as their physical and biological components. Ecosystem diversity is crucial for maintaining the overall functioning of the Earth’s systems. Different ecosystems provide different services and functions, such as carbon sequestration, water purification, and climate regulation. Ecosystem diversity also supports a wide range of species and genetic diversity, as different habitats offer unique conditions and resources for different organisms.
What are the 3 types of biodiversity and explain each type?
Levels of biodiversity. Biodiversity is usually explored at three levels – genetic diversity, species diversity and ecosystem diversity. These three levels work together to create the complexity of life on Earth.
Biodiversity refers to the variety of life forms on Earth, including plants, animals, and microorganisms, as well as the ecosystems in which they exist. It is a crucial aspect of our planet’s health and plays a vital role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems. Biodiversity can be categorized into three main types: genetic diversity, species diversity, and ecosystem diversity.
Genetic diversity is the variation of genes within a species. It is essential for the survival and adaptation of species to changing environments. Genetic diversity allows species to evolve and develop resistance to diseases, pests, and other threats. It also enables species to adapt to different habitats and climates. For example, a diverse gene pool in a crop species can help it withstand drought, pests, and diseases, ensuring food security.
Species diversity refers to the variety of different species in a particular area or ecosystem. It encompasses both the number of species present and their relative abundance. High species diversity is indicative of a healthy and well-functioning ecosystem. Each species has a unique role to play in the ecosystem, and their interactions contribute to the overall stability and productivity of the ecosystem. Loss of species diversity can disrupt these interactions and lead to ecological imbalances.
Ecosystem diversity refers to the variety of different ecosystems or habitats in a given region. It includes terrestrial, aquatic, and marine ecosystems, such as forests, grasslands, wetlands, coral reefs, and rivers. Ecosystem diversity is crucial for maintaining ecological processes, such as nutrient cycling, water purification, and climate regulation. Each ecosystem provides unique services and benefits to humans and other organisms. For example, forests help regulate the climate by absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen, while wetlands act as natural filters, purifying water.
In conclusion, biodiversity encompasses genetic diversity, species diversity, and ecosystem diversity. These three types of biodiversity are interconnected and essential for the functioning and sustainability of ecosystems. Understanding and conserving biodiversity is crucial for preserving the health and well-being of our planet and all its inhabitants.
What are the three levels of biodiversity quizlet?
Three levels of biodiversity would be genetic diversity, species diversity and ecosystem diversity. Genetic diversity is the number of different alleles of genes in a population.
The three levels of biodiversity, as defined by Quizlet, are:
1. Genetic diversity: This level of biodiversity refers to the variety of genes within a species. It encompasses the different versions of genes that exist within a population, allowing for adaptation and evolution. Genetic diversity is crucial for the long-term survival of a species, as it provides the necessary variability for individuals to withstand environmental changes and challenges. It also plays a significant role in the overall health and resilience of ecosystems.
2. Species diversity: Species diversity refers to the variety of different species within a given area or ecosystem. It takes into account the number of different species present, as well as their relative abundance. A high level of species diversity is indicative of a healthy and balanced ecosystem, as it suggests that multiple species are able to coexist and fulfill their ecological roles. Species diversity is important for maintaining ecosystem stability, as each species contributes to the overall functioning of the ecosystem in unique ways.
3. Ecosystem diversity: Ecosystem diversity refers to the variety of different ecosystems or habitats within a region. It encompasses the range of different biotic and abiotic factors present, as well as the interactions between them. Ecosystem diversity is crucial for the overall functioning of the planet, as it provides a wide array of services and resources that support life. Different ecosystems have different characteristics and support different species, making them important for the overall conservation of biodiversity.
The three levels of biodiversity according to Quizlet are genetic diversity, species diversity, and ecosystem diversity. These levels are interconnected and dependent on each other, with genetic diversity providing the foundation for species diversity, and species diversity contributing to ecosystem diversity. Understanding and preserving these levels of biodiversity is essential for the long-term health and sustainability of our planet.
What are the 3 components of biodiversity and discuss each?
Biodiversity is usually explored at three levels – genetic diversity, species diversity and ecosystem diversity. These three levels work together to create the complexity of life on Earth.
Biodiversity refers to the variety of life on Earth, including the different species of plants, animals, and microorganisms, as well as the ecosystems in which they exist. It is a fundamental aspect of our planet’s health and plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems and the overall well-being of the planet. Biodiversity can be divided into three main components, namely genetic diversity, species diversity, and ecosystem diversity.
Genetic diversity refers to the variety of genes within a particular species. It is the result of genetic variations that occur naturally through mutations, genetic recombination, and other processes. Genetic diversity is essential for the survival and adaptation of species to changing environmental conditions. It allows for the development of traits that can help species withstand diseases, pests, and other threats. Additionally, genetic diversity is crucial for the long-term viability of populations, as it reduces the risk of inbreeding and increases the chances of successful reproduction.
Species diversity refers to the variety of different species within a particular ecosystem or on the entire planet. It encompasses the number of species present, as well as their relative abundance. Species diversity is a measure of the overall health and stability of an ecosystem. High species diversity indicates a well-functioning ecosystem with a wide range of ecological niches and interactions. It also provides resilience to disturbances, as the loss of one species can be compensated by others. Species diversity is important for ecosystem services, such as pollination, nutrient cycling, and pest control.
Ecosystem diversity refers to the variety of different ecosystems present on Earth. An ecosystem is a complex network of living organisms, their physical environment, and the interactions between them. Ecosystem diversity includes different types of habitats, such as forests, grasslands, wetlands, deserts, and coral reefs. Each ecosystem has its unique set of species and ecological processes. Ecosystem diversity is crucial for the overall functioning of the planet, as it provides various ecosystem services, including climate regulation, water purification, and soil formation. It also supports the livelihoods of millions of people who depend on natural resources for their survival.
What are 3 ways biodiversity is important?
Biodiversity is essential for human health and well-being, economic prosperity, food safety and security, and other areas critical to all humans and all human societies.
Biodiversity refers to the variety of life forms found on Earth, including plants, animals, and microorganisms. It is a crucial aspect of our planet’s health and plays a vital role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems. Biodiversity is important for several reasons, and in this answer, we will explore three key ways in which it contributes to the well-being of our planet and its inhabitants.
Firstly, biodiversity is essential for the functioning of ecosystems. Each species within an ecosystem has a specific role to play, and the interactions between different species are what keep the ecosystem in balance. For example, plants provide oxygen and food for animals, while animals help in pollination and seed dispersal. If a species becomes extinct, it can disrupt the delicate balance of the ecosystem, leading to a cascade of negative effects on other species and the overall functioning of the ecosystem.
Secondly, biodiversity is crucial for human well-being. Many of the resources we rely on, such as food, medicine, and clean water, are derived from biodiversity. For instance, a diverse range of crops ensures food security and provides a variety of nutrients for a healthy diet. Additionally, many medicines are derived from plants and animals, with countless life-saving drugs being discovered through the study of biodiversity. Furthermore, diverse ecosystems also provide important services such as water purification, climate regulation, and flood control.
Lastly, biodiversity has intrinsic value and is a source of wonder and inspiration for humans. The sheer diversity of life forms on our planet is awe-inspiring and has captivated humans for centuries. Biodiversity provides us with opportunities for recreation, education, and spiritual fulfillment. It enriches our lives and connects us to the natural world, reminding us of our place in the intricate web of life.
Biodiversity is of utmost importance for the functioning of ecosystems, human well-being, and our connection to the natural world. It is essential that we recognize and appreciate the value of biodiversity and take steps to conserve and protect it for future generations.
What are 3 things biodiversity provides us with?
Biodiversity provides us with drinking water, oxygen to breathe, food, medicine, decomposition of waste, and helps our planet withstand natural disasters.
Biodiversity refers to the variety of life on Earth, including the different species of plants, animals, and microorganisms, as well as the ecosystems in which they exist. It is a fundamental aspect of our planet’s health and provides numerous benefits to human beings. Here are three important things that biodiversity provides us with:
1. Ecosystem Services: Biodiversity plays a crucial role in providing essential ecosystem services that are vital for human well-being. These services include the purification of air and water, regulation of climate, pollination of crops, and decomposition of waste. For example, forests act as natural filters, absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen, helping to mitigate climate change. Wetlands help to purify water by filtering out pollutants and excess nutrients, ensuring a clean water supply for human consumption.
2. Food and Medicine: Biodiversity is the foundation of our food systems and provides us with a wide variety of crops, livestock, and seafood. Different plant and animal species contribute to the diversity of our diets, ensuring a balanced and nutritious intake of food. Additionally, many medicinal drugs are derived from natural sources, such as plants and microorganisms found in diverse ecosystems. Biodiversity is a valuable resource for the development of new medicines and treatments for various diseases.
3. Cultural and Recreational Value: Biodiversity is deeply intertwined with human culture and provides us with aesthetic, spiritual, and recreational value. Natural landscapes, diverse ecosystems, and the presence of different species contribute to the beauty and uniqueness of our surroundings. Biodiversity also plays a significant role in traditional practices, rituals, and ceremonies of indigenous communities around the world. Furthermore, many people find joy and relaxation in activities such as birdwatching, hiking, and wildlife photography, which rely on the presence of diverse species.
Biodiversity provides us with essential ecosystem services, a diverse range of food and medicine, and cultural and recreational value. It is crucial for the sustainability and well-being of both human beings and the planet as a whole. Therefore, it is essential to protect and conserve biodiversity to ensure a healthy and prosperous future for all.
Can you explain the concept of biodiversity and its importance?
Biodiversity refers to the variety of life forms, including plants, animals, and microorganisms, that exist in a particular habitat or on Earth as a whole. It encompasses the diversity of genes, species, and ecosystems. Biodiversity is crucial for the functioning and stability of ecosystems, as well as for the well-being of human societies.
Firstly, biodiversity plays a fundamental role in maintaining ecosystem services, such as pollination, nutrient cycling, and water purification. These services are essential for human survival and provide us with food, clean air, and clean water. Secondly, biodiversity contributes to the resilience and adaptability of ecosystems. A diverse range of species ensures that if one species is affected by a disturbance or environmental change, others can step in and fulfill similar ecological roles. This resilience helps ecosystems withstand and recover from disturbances, such as natural disasters or climate change.
What are the three levels of biodiversity and how do they contribute to overall ecosystem health?
The three levels of biodiversity are genetic diversity, species diversity, and ecosystem diversity. Genetic diversity refers to the variety of genes within a species, which allows for adaptation and survival in changing environments. It provides the raw material for evolution and enables species to respond to environmental pressures, such as diseases or climate change.
Species diversity, on the other hand, refers to the variety of different species within a particular habitat or ecosystem. It is important for ecosystem health because each species has a unique role or niche in the ecosystem. A higher species diversity means that there are more interactions and connections within the ecosystem, leading to increased stability and resilience. Additionally, species diversity can also indicate the overall health of an ecosystem. A decline in species diversity may indicate environmental degradation or habitat loss.
Ecosystem diversity refers to the variety of different ecosystems or habitats within a region or on Earth as a whole. It is important because different ecosystems provide different services and support different species. Ecosystem diversity contributes to overall ecosystem health by ensuring that a range of habitats and resources are available for different species to thrive. It also enhances the resilience of ecosystems by providing alternative habitats for species in case of disturbances or changes in environmental conditions.
What are the three levels of biodiversity and how do they contribute to overall ecosystem health?
Biodiversity refers to the variety of life on Earth, including the diversity of species, genetic diversity within species, and the diversity of ecosystems. These three levels of biodiversity are interconnected and play a crucial role in maintaining the health and functioning of ecosystems.
The first level of biodiversity is species diversity, which refers to the variety of different species within a given area. A higher species diversity is generally associated with a healthier ecosystem as it indicates a more balanced and stable community. Each species has its own unique role and function within an ecosystem, and a diverse community of species ensures that all ecological niches are filled. This helps to maintain important ecological processes such as nutrient cycling, pollination, and pest control.
The second level of biodiversity is genetic diversity, which refers to the variation in genes within a species. Genetic diversity is important for the survival and adaptation of species to changing environmental conditions. A higher genetic diversity allows for a greater range of traits within a species, increasing its ability to respond to environmental changes such as climate change or the introduction of new diseases. Genetic diversity also plays a crucial role in the long-term survival of species by reducing the risk of inbreeding and increasing the overall fitness of populations.
How does genetic diversity play a role in the survival and adaptation of species?
Genetic diversity refers to the variety of genes within a species or population. It is crucial for the survival and adaptation of species because it provides the raw material for evolution. When a population has high genetic diversity, it means that there is a wide range of genetic variations present. This variation allows for a greater chance of individuals possessing traits that are advantageous for survival in changing environments.
Genetic diversity plays a key role in the survival of species in several ways. First, it increases the likelihood that some individuals will have traits that enable them to withstand environmental changes or resist diseases. For example, if a population of plants has high genetic diversity, some individuals may have genes that make them resistant to a particular pest or disease. This genetic variation ensures that even if some individuals are affected, others will survive and reproduce, maintaining the overall population.
Second, genetic diversity allows for adaptation to new environments. When a species faces a new environmental challenge, individuals with certain genetic traits may be better suited to survive and reproduce. Over time, these individuals pass on their advantageous genes to future generations, leading to the adaptation of the species to the new environment. Without genetic diversity, a species may lack the necessary genetic variations to adapt and may face a higher risk of extinction.
Can you provide examples of how species diversity impacts ecosystem stability and resilience?
Species diversity is crucial for maintaining ecosystem stability and resilience. One example of this is the role of species diversity in pest control. In agricultural systems, having a variety of plant species can help prevent the outbreak of pests. This is because different plant species attract different types of pests, and by having a diverse range of plants, the pests are less likely to reach damaging levels. Additionally, some plant species may attract natural predators of pests, further helping to control their populations. Therefore, by promoting species diversity, we can reduce the need for chemical pesticides and promote a more sustainable and resilient agricultural system.
Another example of how species diversity impacts ecosystem stability is through the process of pollination. Many plants rely on pollinators, such as bees and butterflies, to transfer pollen between flowers and enable reproduction. However, different plant species have different pollination requirements, such as specific types of pollinators or specific flower structures. Therefore, having a diverse range of plant species ensures that there are enough resources available for a variety of pollinators, which in turn helps to maintain their populations. Without sufficient pollinators, many plant species would struggle to reproduce, leading to a decline in overall ecosystem health.
What are the potential consequences of a decline in biodiversity at all three levels?
A decline in biodiversity at all three levels – genetic diversity, species diversity, and ecosystem diversity – can have significant consequences for the health and functioning of ecosystems. Firstly, a decrease in genetic diversity can make species more vulnerable to diseases and environmental changes. When a population has low genetic diversity, it means that individuals are more genetically similar, making them more susceptible to the same threats. This can lead to a higher risk of extinction, as a single disease or environmental disturbance can wipe out the entire population.
Secondly, a decline in species diversity can disrupt the balance and stability of ecosystems. Each species plays a unique role in the ecosystem, and their interactions with other species are crucial for maintaining the overall health and functioning of the ecosystem. When species diversity decreases, it can lead to imbalances in predator-prey relationships, competition for resources, and disruptions in nutrient cycling. This can result in a decrease in ecosystem productivity and resilience, making it more difficult for the ecosystem to recover from disturbances.
Lastly, a decline in ecosystem diversity can have far-reaching consequences for human well-being. Ecosystems provide a wide range of services, such as clean air and water, pollination of crops, and regulation of climate. When ecosystem diversity declines, these services can be compromised, leading to negative impacts on human health, food security, and economic stability. Additionally, a loss of diverse ecosystems can also result in the loss of potential sources for new medicines and other valuable resources.

Conclusion
Biodiversity refers to the variety of life forms on Earth, including plants, animals, and microorganisms. It encompasses the genetic, species, and ecosystem diversity that exists within a given area. Understanding and preserving biodiversity is crucial for maintaining the health and balance of ecosystems, as well as for the well-being of human populations. Biodiversity can be categorized into three levels, namely genetic diversity, species diversity, and ecosystem diversity.
Genetic diversity is the variation in genes within a species. It is the result of genetic mutations, recombination, and natural selection. Genetic diversity is important because it allows species to adapt to changing environmental conditions and increases their chances of survival. It also provides the foundation for evolution, as it enables the development of new traits and characteristics over time. Genetic diversity can be measured by analyzing the number of different alleles present in a population or by studying the DNA sequences of individuals.
Species diversity refers to the variety of different species within a given area. It includes both the number of species present and their relative abundance. Species diversity is influenced by factors such as habitat availability, climate, and interactions between species. High species diversity is often associated with healthy and resilient ecosystems, as it ensures a greater range of ecological functions and services. It also provides opportunities for ecological interactions, such as predation, competition, and mutualism, which contribute to the stability and productivity of ecosystems.
Ecosystem diversity is the variety of different ecosystems within a region or on a global scale. An ecosystem is a community of organisms interacting with each other and their physical environment. Ecosystem diversity is influenced by factors such as climate, topography, and geological history. It encompasses a wide range of habitats, from forests and grasslands to wetlands and coral reefs. Each ecosystem has its own unique set of species and ecological processes, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the planet.
Learn about the three levels of biodiversity – genetic, species, and ecosystem diversity. Discover how these levels contribute to the overall health and balance of our planet’s ecosystems.



